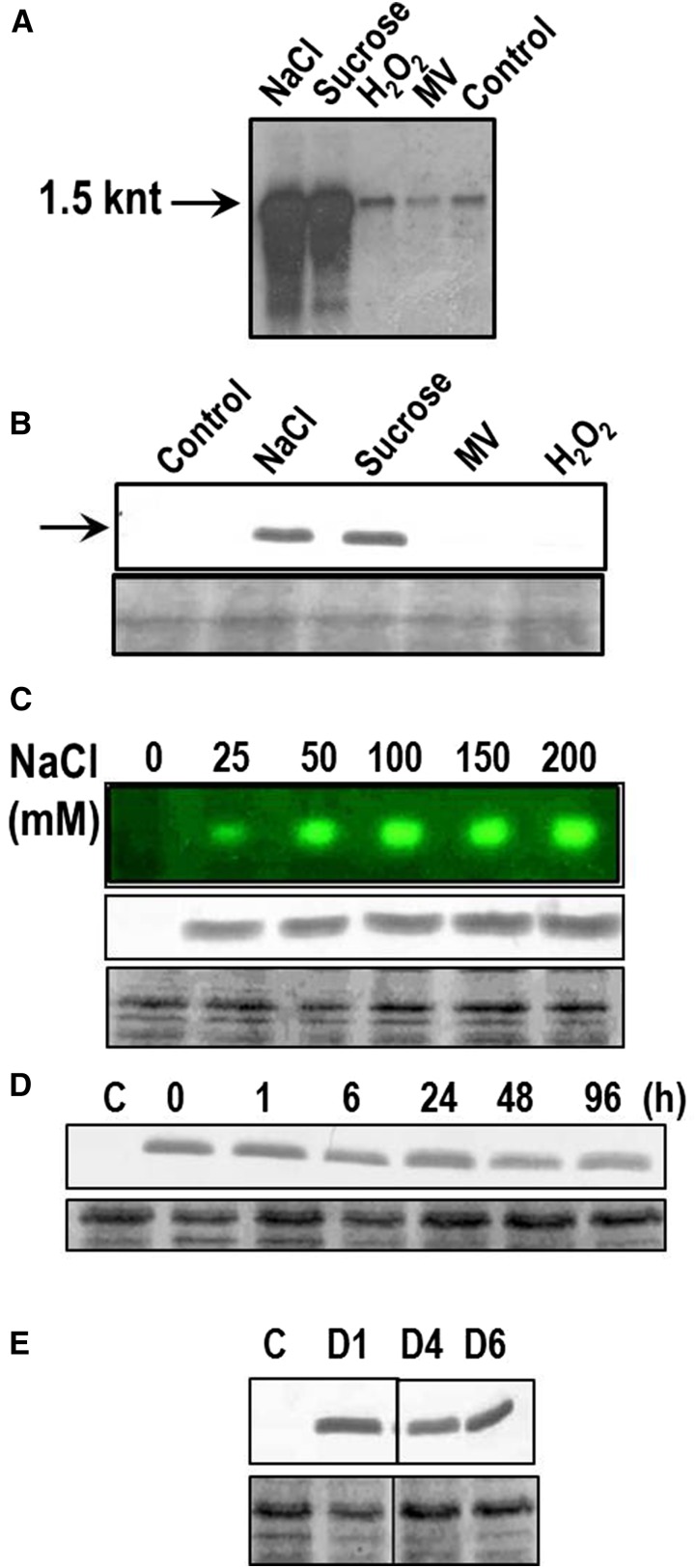
Figure 3.
Expression analysis of KatB under different abiotic stresses. A, Northern-blotting hybridization analysis. Total RNA was isolated from untreated Anabaena PCC 7120 (control) or from cells treated with 150 mm NaCl, 300 mm Suc, 1 mm H2O2 (H2O2), or 2 μm MV. Subsequently, RNA (5 μg/lane) was resolved on formaldehyde-agarose gels, transferred onto a nylon membrane, and probed with the DIG-labeled katB ORF. The approximately 1.5-knt transcript is shown by an arrow. The northern blotting-hybridization experiment was repeated four times with consistent results. B, Induction of the KatB protein in Anabaena. Total proteins (20 μg/lane) were isolated from Anabaena cells treated with 150 mm (NaCl) or 300 mm (Suc) or 2 μm (MV) or 1 mm H2O2 (H2O2) and probed with the KatB antiserum (1:10,000 dilution). The 20-kD KatB protein is shown by an arrow. C, Anabaena cells were treated with different concentrations of NaCl as indicated in the figure for 20 h. Subsequently, cell-free extracts were prepared and employed for zymographic analysis (top) or probed with the KatB antiserum on western blots (middle). Representative zymogram is depicted and the Ponceau S-stained part of the nitrocellulose membrane is shown as loading control at the bottom. D, Stability of the KatB protein. Anabaena cells were exposed to 150 mm NaCl for 16 h, thoroughly washed, reinoculated in medium lacking NaCl, and the KatB protein content was monitored on western blots with the KatB antiserum at different intervals of time as indicated. The Ponceau S-stained loading control is shown at the bottom. E, KatB expression in response to desiccation. Cell-free extracts of the control Anabaena cells (C) or the desiccated Anabaena cells after 1 d (D1), 4 d (D4), or 6 d (D6) were probed with the KatB antiserum on western blots. The Ponceau S-stained loading control is shown at the bottom.