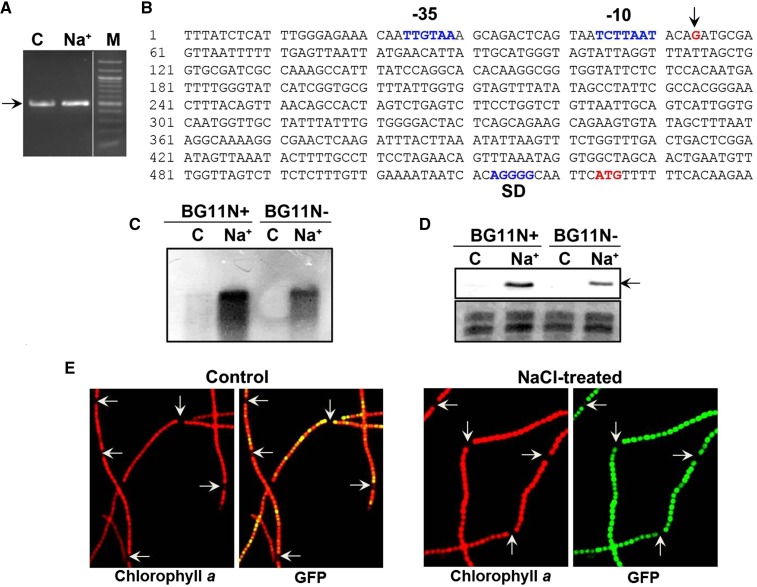
Figure 4.
RACE analysis and expression of the katB promoter-gfp gene fusion (pAM3090prom). A, RACE was performed with RNA isolated from control Anabaena cells (C) or cells treated with 150 mm NaCl (Na+) for 16 h. The approximately 450-bp DNA fragment is shown by an arrow. Then 20 µL and 5 µL of the PCR reaction was loaded in the C and Na+ lane, respectively. M, 100-bp DNA marker. B, Sequence analysis of the RACE product. The transcriptional start site (G, in red color) is indicated by an arrow. The nucleotide sequence corresponding to the −10 and −35 region of the katB promoter, the ribosome binding site (SD), and the translational start codon (ATG) are denoted. C, The wild-type Anabaena PCC 7120 cells grown in BG11 medium with (BG11N+) or without combined nitrogen (BG11N-) were treated with 150 mm NaCl (Na+). The untreated cells (C) served as control in both types of media. RNA was isolated from both control (C) and treated (Na+) cells and resolved on formaldehyde-agarose gel, transferred onto anylon membrane, and probed with the DIG-labeled katB DNA. D, Protein extracts (60 μg/lane) from the control (C) and treated (Na+) Anabaena PCC 7120 cells grown in BG11N+ or BG11N- were resolved by SDS-PAGE (14% gel) and probed with the KatB antiserum on western blots. The 26-kD KatB protein is depicted by an arrow. E, Fluorescence micrographs (1500×). An3090prom cells were grown in medium without combined nitrogen (BG11N-) and treated with NaCl. Anabaena filaments were visualized under a fluorescence microscope using Hg-Arc lamp; chlorophyll a fluorescence (excitation BP, 546–612 nm and emission LP, 515 nm), and GFP fluorescence (excitation BP, 450–490 nm and emission LP, 515 nm). Heterocysts are depicted by arrows.