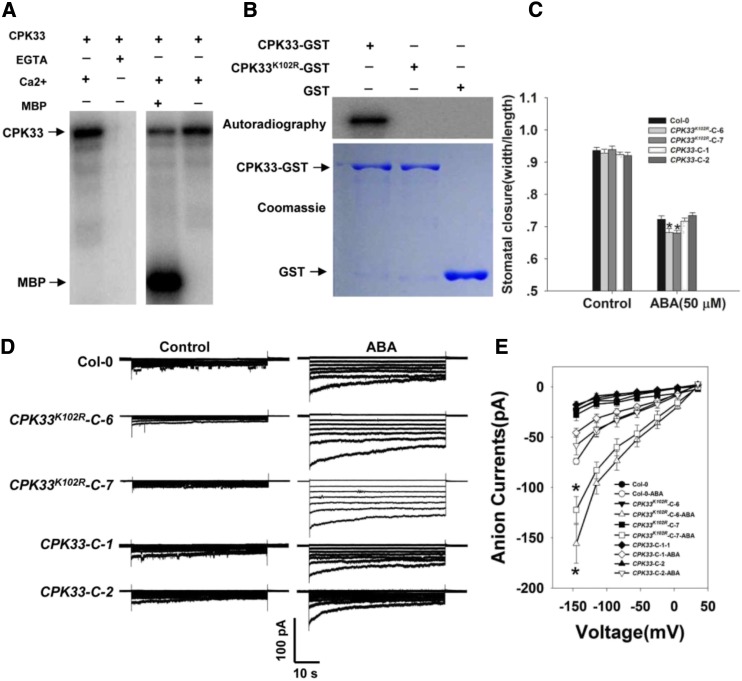
Figure 7.
The kinase activity of CPK33 is required for stomatal closure and the regulation of slow type anion channels. A, In vitro assay of CPK33 kinase activity. Left: Lanes 1 and 2 show the autophosphorylation activity of CPK33-GST in the presence/absence of 1 mm free Ca2+ and the presence of 2 mm EGTA. Right: Lanes 3 and 4 show the phosphorylation of MBP by CPK33-GST. B, In vitro kinase activity of CPK33K102R. Top: The autophosphorylation of purified CPK33-GST and CPK33K102R-GST. Bottom: SDS-PAGE separation of purified CPK33-GST, CPK33K102R-GST, and GST (arrowed). C, ABA-promoted stomatal closure. Error bars represent the se (n = 3). At least 60 stomata were measured for each genotype per replication. D, ABA-activated slow type anion channels in guard cell protoplasts. Time and voltage scales are as shown. E, Current/voltage relationships of whole-cell slow anion currents as illustrated in D. The numbers of guard cells measured were: Col-0 (10), Col-0-ABA (9), CPK33-C-1 (8), CPK33-C-1-ABA (8), CPK33-C-2 (8), CPK33-C-2-ABA (9), CPK33K102R-C-6 (9), CPK33K102R-C-6-ABA (8), CPK33K102R-C-7 (7), and CPK33K102R-C-7-ABA (10). Data are shown in the form mean ± se. Asterisks in C and E indicate significant differences between means (P < 0.05).