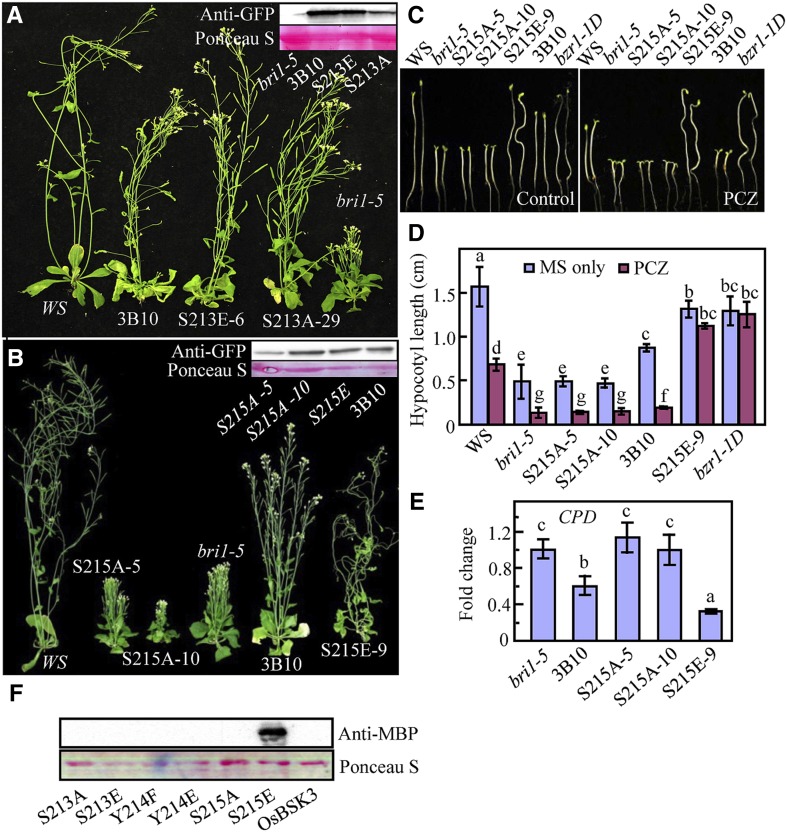
Figure 4.
Functional analysis of the OsBSK3 phosphorylation sites in Arabidopsis. A and B, Eight-week-old wild type (Ws), bri1-5 mutant, and bri1-5 mutant overexpressing wild type or a mutated form (S213A, S213E, S215A, and S215E) of OsBSK3. Immunoblotting for the expression of various OsBSK3 forms was conducted using anti-GFP antibodies since the OsBSK3s were produced with a C-terminal YFP tag. Ponceau S staining for the Rubisco large subunit was used as an equal loading control. C, The S215E transgenic plants were insensitive to PCZ-inhibited hypocotyl elongation. Young seedlings of wild type (Ws), bri1-5, or bri1-5 overexpressing various OsBSK3 forms were grown in the dark for 5 d on regular medium or medium containing 0.25 μm PCZ. D, A quantitative analysis of the hypocotyls of the seedlings shown in C. Each value in the graph represents the average of at least 20 individual seedlings. Error bars represent the se. E, Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the CPD expression levels in the seedlings shown in B. Error bars represent ± sd. F, A gel overlay analysis of the interaction between AtBSU1 and the various OsBSK3 mutant proteins. GST-tagged OsBSK3 proteins were immunoblotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with MBP-AtBSU1 and horseradish peroxidase-labeled anti-MBP antibodies. Total protein was visualized by Ponceau S staining. A one-way ANOVA was performed in D and E; statistically significant differences are indicated by different lowercase letters (P < 0.05).