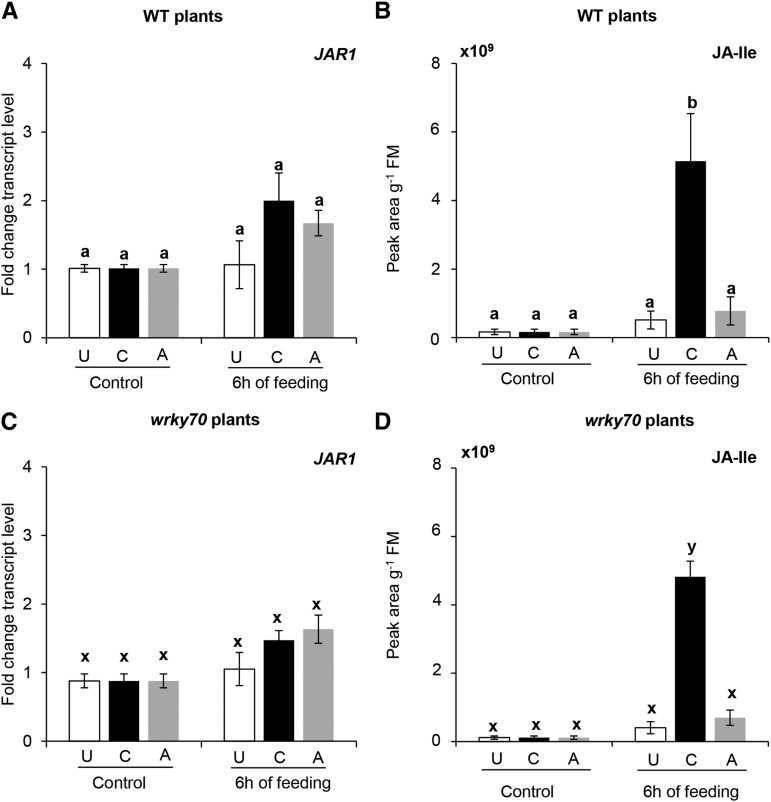
Figure 3.
Transcript levels of JASMONIC ACID AMIDO SYNTHETASE1 (JAR1), a JA-Ile biosynthetic gene, and JA-Ile levels in response to subsequent caterpillar feeding in unexposed (U), caterpillar-exposed (C), and aphid-exposed (A) wild-type (WT) and wrky70 plants. A and C, Means ± se (n = 5) of JAR1 relative transcript levels in unexposed, caterpillar-exposed, and aphid-exposed wild type and wrky70 mutant plants before and after 6 h of subsequent feeding of five first instar larvae of P. brassicae. Relative transcript levels of JAR1 were determined by RT-qPCR. The value at each time point represents the expression of JAR1 relative to the EF1α gene in wild-type and wrky70 plants. B and D, Means ± se (n = 5) of JA-Ile levels in unexposed, caterpillar-exposed, and aphid-exposed wild-type and wrky70 mutant plants before and after 6 h of subsequent feeding by five first instar larvae of P. brassicae. JA-Ile levels were determined by LC-MS followed by quantifying peak areas. Mean values of JAR1 relative transcripts and JA-Ile levels from unexposed, caterpillar-exposed, and aphid-exposed treatment were compared among treatments within the same plant background (wild-type and wrky70 plants) by one-way ANOVA by Tukey’s HSD posthoc test; different letters indicate significant differences within a plant genotype (P ≤ 0.05). FM, Fresh mass.