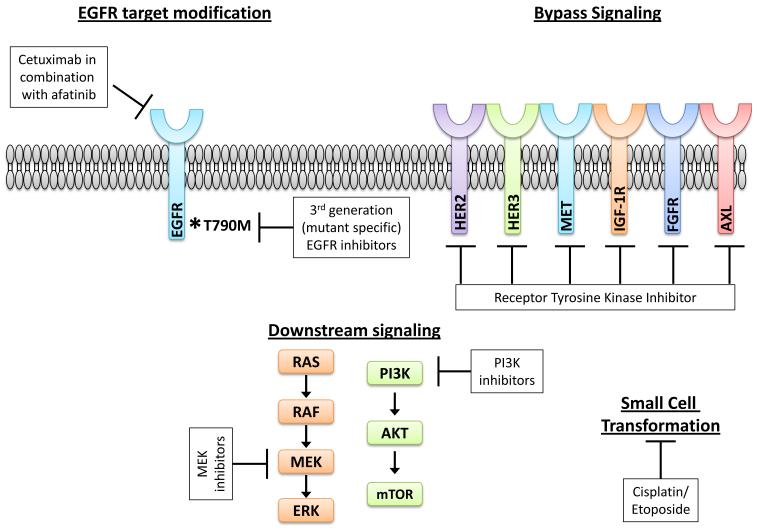
Figure 1. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR TKIs in EGFR mutant NSCLC.
Resistance can be mediated by EGFR target modifications, most commonly the EGFR T790M second-site mutation, through bypass signaling pathways which circumvent the inhibited driver oncogene (EGFR), and through histological transformation (in this case, change in histology from NSCLC to SCLC). Potential strategies to overcome resistance are noted in the white boxes.