Figure 2.
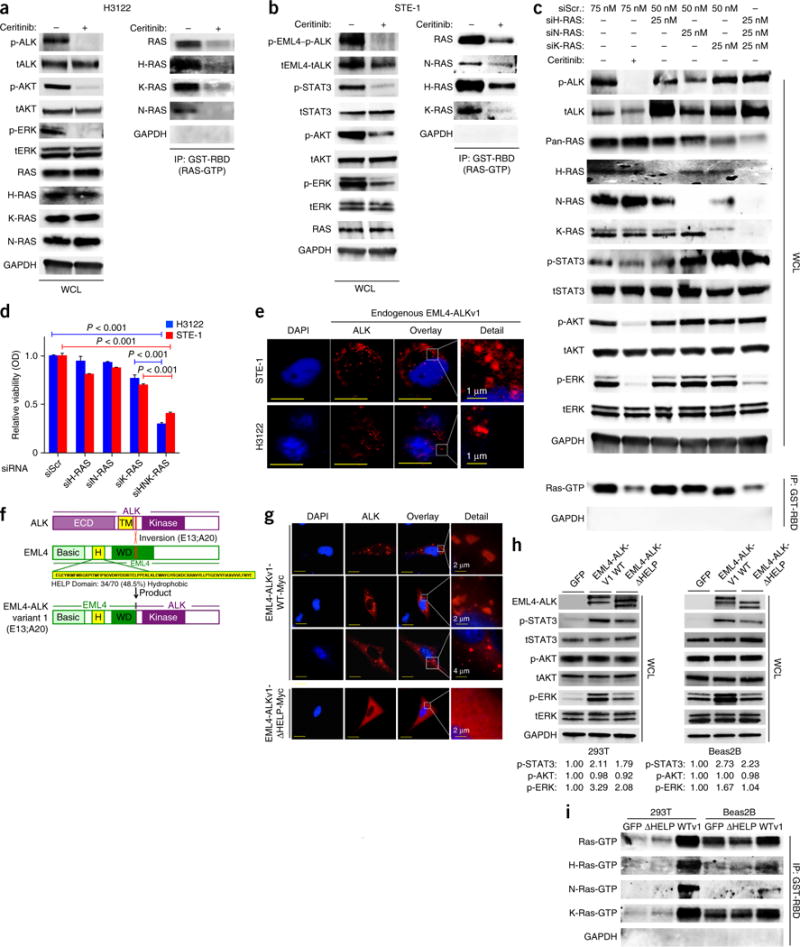
Cells expressing EML4-ALK (E13:A20, variant 1) activate H-, N- and K-RAS to drive MAPK signaling, via the HELP domain of EML4. (a,b) Immunoblot analysis, with antibodies against the indicated molecules, of whole-cell lysates (WCL) or GST-RBD-immunoprecipitated (IP) lysates of H3122 (a) and STE-1 (b) cells treated for 30 min with 200 nM ceritinib (+) or not (−). (c) Immunoblot analysis, with antibodies against the indicated molecules, of WCL or GST-RBD IP lysates of cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (siScr) or siRNA directed against H-RAS (siH-RAS), N-RAS (siN-RAS) or K-RAS (siK-RAS) and treated with 200 nM ceritinib (+) or DMSO (−) for 30 min. (d) Crystal violet assay of cell cultures treated as in c or with siRNA directed against all three RAS isoforms (siHNK-RAS) OD, optical density. P < 0.001 (unpaired t-test). (e) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous EML4-ALK in STE-1 and H3122 cells with antibody against ALK. Red shows EML4-ALK expression; blue shows DAPI nuclear staining. Inset (far right) shows high magnification of EML4-ALK localization. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown. Scale bars indicate 10 μM. (f) Schematic of ALK (top), showing the extra-cellular domain (ECD) and transmembrane domain (TM), as well as the E13;A20 inversion (below); EML4 (middle), showing the hydrophobic HELP domain (H) and WD-repeat domain (WD); and the EML4-ALK variant 1 (E13:A20) (bottom). (g) Immunofluorescence staining of overexpressed Myc-tagged EML4-ALKWT (EML4-ALKv1-WT-Myc) or ΔHELP EML4-ALK (EML4-ALKv1-ΔHELP-Myc) with antibody against the Myc tag in Beas2B cells. Red shows EML4-ALK expression; blue shows DAPI nuclear staining. Inset (far right) shows high magnification of EML4-ALK localization. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown. Scale bars indicate 15 μm. (h) Immunoblot analysis, with antibodies against the indicated molecules, of lysates of Beas2B and 293T cells transfected with the indicated constructs. Below, expression of each phosphorylated protein relative to that in the GFP-control condition, assessed by densitometry. (i) GST-RBD pulldown assays to isolate Ras-GTP, with immunoblotting using RAS isoform-specific antibodies, in the cells in h. Data shown are n = 3, ±s.e.m., for quantitative assays and for immunoblot assays representative of three independent experiments.
