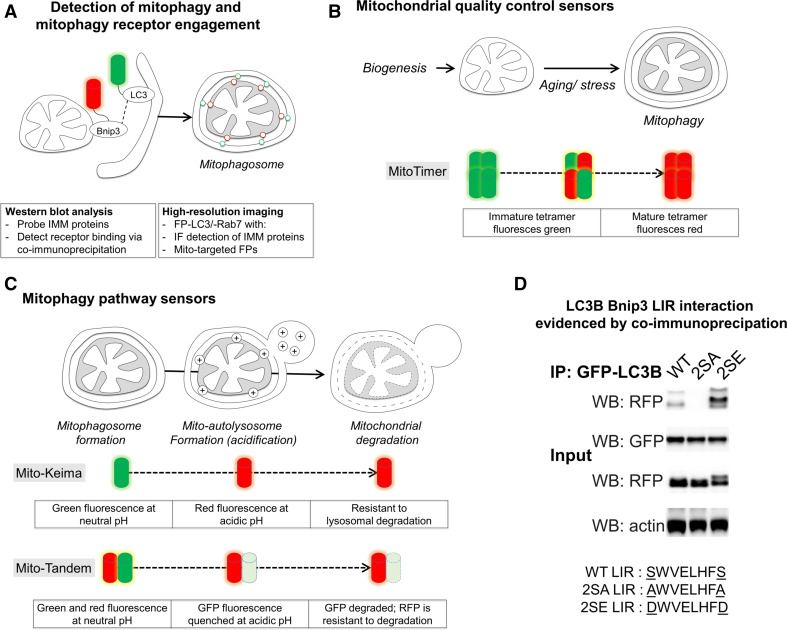
Fig. 8.
Methodologies to measure mitophagy. Biochemical and imaging-based assays can measure different aspects of mitophagy program activities. a Mitochondria-containing autophagosomes can be detected via imaging of fluorescent protein (FP)-LC3-labeled autophagosome colocalization with immunofluorescence or FP-labeled mitochondria. Western blot and immunofluorescence detection of IMM and matrix proteins is most specific for detecting mitophagic degradation events. Mito-autolysosomes can be detected using FP-Rab7. b MitoTimer is a tetramer which matures as a green-to-red fluorescent protein. MitoTimer can be used under inducible- and constitutive-expression to analyze mitochondrial quality control dynamics. c Mitochondrial entry into the autolysosome and subsequent degradation can be measured using FP sensors targeted to mitochondria, that are sensitive to low pH and resistant to degradation by lysosomal hydrolases. Mito-Keima fluoresces green at neutral pH in the cytosol, and red upon entry into acidic autolysosomes. Mito-Tandem is a mitochondria-targeted RFP–GFP fusion. GFP fluorescence is acid-quenched while RFP fluorescence remains stable also at low pH, permitting live cell analysis of mitochondrial presence in autolysosomes. Note, lysosomal hydrolases degrade GFP more efficiently than RFP, permitting detection of mitophagy in fixed cells. d Example co-immunoprecipitation demonstrating phospho-regulated Bnip3 mitophagy receptor engagement, i.e., Bnip3 LIR binding with LC3B. MCF7 cells stably expressing GFP-LC3B were transfected with RFP-Bnip3 WT, or LIR-inactive 2SA or LIR-activated 2SE mutants. At 48 h of expression, co-immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed with anti-GFP antibody-coupled magnetic beads. Whole cell lysates (input) and IP samples were analyzed by western blotting (WB). This research was originally published in Zhu et al. [52]. © The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology