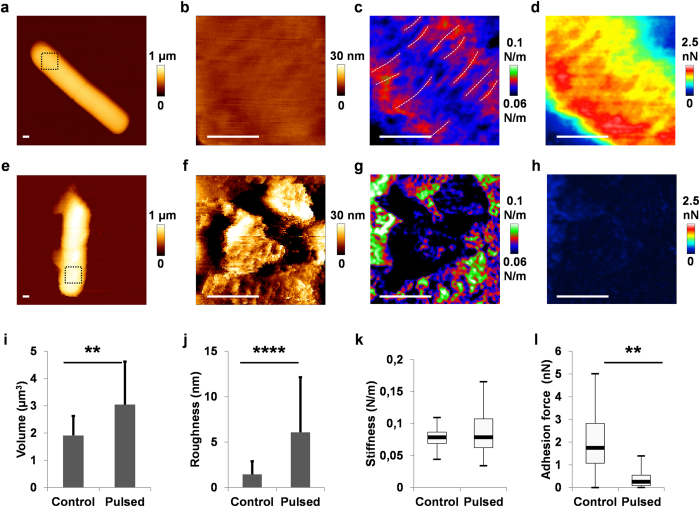
Figure 3. PEF-induced morphological, mechanical and physical damage to cell wall.
(a,e) Examples of vegetative bacteria visualized by AFM; inset shows location of height resolution image (b,f), stiffness map (c,g) and adhesion force map (d,h) measured by hydrophobic interactions; from an untreated bacterium (a–d) and a pulsed bacterium (e–h) with 1000 micropulses at 7.5 kV/cm. Scale bars: 200 nm. (i) Statistical analysis of the bacterial volume. PEF exposure induces swelling of bacteria. The measurements for each condition were performed on four replicates with at least 30 bacteria each. (j) Statistical analysis of roughness. Roughness increased after PEF. The roughness values (Ra) were calculated for each condition from 30 bacteria in four experiments. (k) Statistical analysis of the stiffness. PEF increased the heterogeneity of stiffness. Box plots were obtained from stiffness maps of 1024 curves from 15 bacteria per condition. (l) Statistical analysis of hydrophobicity. Loss of hydrophobicity was noted after PEF. For each condition, box plots were determined with adhesion maps of 16384 curves from seven bacteria from two independent experiments.