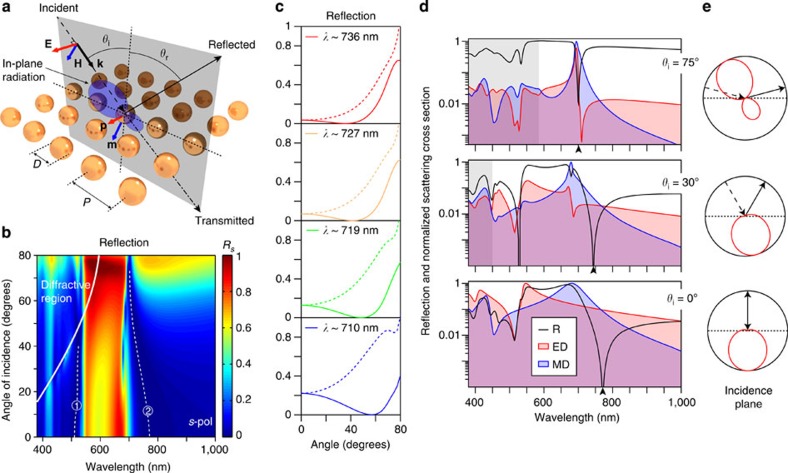
Figure 4. Simulated optical response of arrays of silicon spheres under s-polarized oblique incidence.
(a) Scheme of the simulated system. (b) Numerically calculated reflection versus wavelength and angle of incidence for a square array of silicon spheres with diameter D=180 nm and pitch P=300 nm. The region for which diffraction appears is indicated and delimited by the thick, solid white line. The white dashed lines are guides to the eye to help identifying the low reflectivity regions of interest. (c) Reflection versus angle of incidence for selected wavelengths showing Brewster's angle for s-polarization. Solid lines represent s-polarization while dashed lines are the corresponding curves for p-polarization. Dependence on wavelength and the possibility to achieve values below 45° are observed. (d) Reflection (black curve) and electric dipole (red curve and corresponding shaded area, electric dipole (ED)) and magnetic dipole (blue curve and corresponding shaded area, magnetic dipole (MD)) contributions to the scattering (normalized to their common maximum) from a single sphere in the array for several angles of incidence. Log10 scale is used for better visualization of the minima. Diffractive regions are indicated by the shaded grey area. (e) Associated radiation patterns of each single particle in the array in the plane of incidence at the wavelengths of minimum reflection (arrow heads in d).