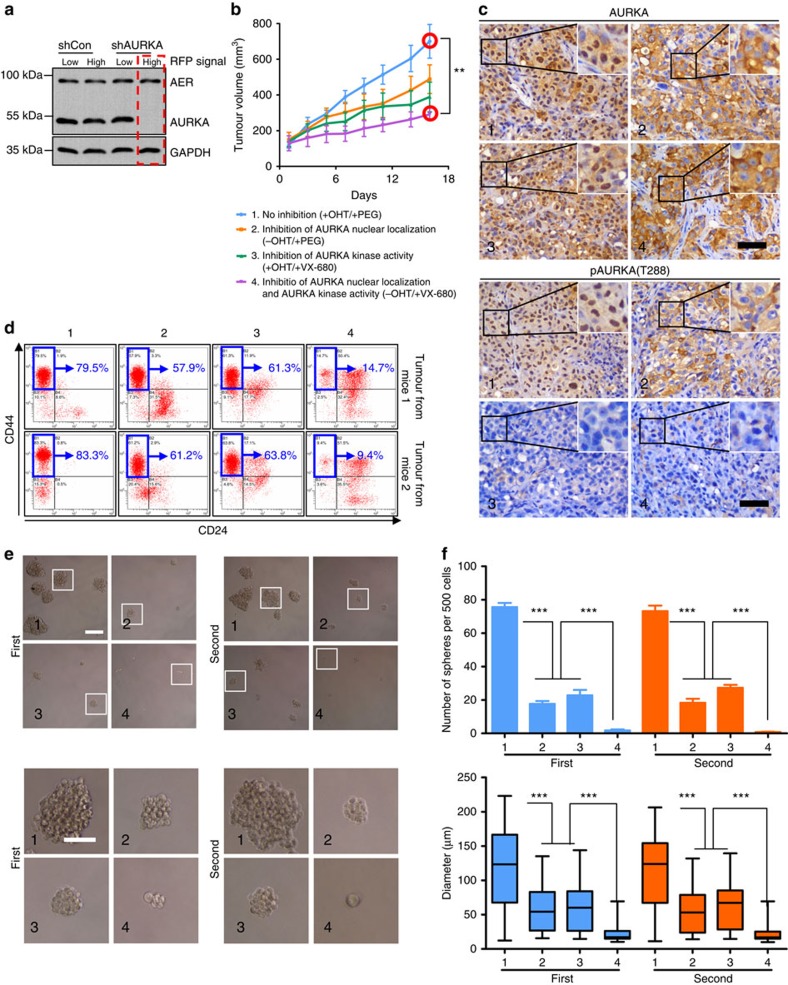
Figure 6. Blocking AURKA nuclear translocation enhances the anticancer effects of Aurora kinase inhibitor.
(a) MDA-MB-231 cells expressing AURKA-ER were infected with lentiviral expressing AURKA shRNA or control. The cells were sorted for RFP (+) and the lysates were examined via immunoblotting (IB). (b) MDA-MB-231 cells sorted from a (red rectangle) were inoculated subcutaneously in nude mice. Mice treated with OHT were then administered the indicated treatments via intraperitoneal injection. Data were presented as the means±s.e.m.; n=5 per group. The statistical significance between tumour volumes was calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's multiple comparison tests (group1 versus group4). See also Supplementary Methods. (c) IHC staining was performed on tumours harvested at the end of the animal experiment (b). Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Flow cytometry for the expression of CD44 and CD24 on single cells from tumour xenografts. (e) Mammosphere formation by single-cell suspensions derived from tumour xenografts (left panel). The mammosphere were used to perform a secondary passage (right panel). (f) Quantification of the diameters of the spheres from e. The upper panel shows the number of Φ>60 μm mammospheres. Statistical comparison was performed (lower panel) using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test (***P<0.001). Data are presented as the means±s.e.m. of three independent experiments (analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by least significant difference (LSD) test; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001).