Table 1. Comparison of the photocurrent and electronic properties of different compositions of PNT.
| Structures | 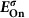 |
σMax | GMax | P | 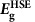 |
ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (eV) | (10−4 V−1) | (10−9 cm V−1) | (C m−2) | (eV) | meV | |
| PbTiO3 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 12.0 | 0.81 | 2.71 | — |
| 1 × 1 × 2 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 3.6 | 0.73 | 1.58 | 0 |
| Rock salt | 2.1 | 6.1 | 11.0 | 0.96 | 2.05 | +30 |
| 1 × 1 × 3 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 14.0 | 0.91 | 1.58 | — |
| 1 × 1 × 4 | 1.6 | 4.7 | 29.7 | 1.10 | 1.33 | — |
| 1 × 1 × 5 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 36.9 | 1.07 | 1.28 | — |
| 1 × 1 × 6 | 1.5 | 6.7 | 46.8 | 1.05 | 1.08 | — |
Calculated shift current onset energy 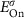 , maximum shift current susceptibility σMax, maximum Glass coefficient GMax, polarization P and Heyd-Scuseria-Ernzerhof (HSE) hybrid functional bandgap
, maximum shift current susceptibility σMax, maximum Glass coefficient GMax, polarization P and Heyd-Scuseria-Ernzerhof (HSE) hybrid functional bandgap 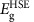 of the layered and rock salt PNT. ΔE (meV per atom) is the relative stability of different cation arrangements that have the same composition. PbTiO3 values are also shown for comparison. Maximum values are for energies smaller than 3.0 eV (E<4.0 eV for PbTiO3).
of the layered and rock salt PNT. ΔE (meV per atom) is the relative stability of different cation arrangements that have the same composition. PbTiO3 values are also shown for comparison. Maximum values are for energies smaller than 3.0 eV (E<4.0 eV for PbTiO3).
