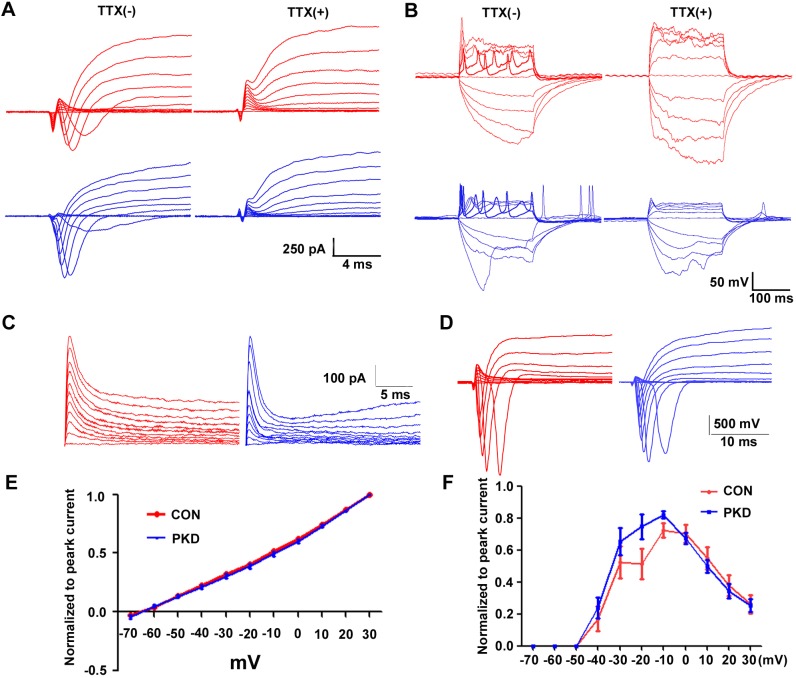
Fig. 5.
Electrophysiological properties of PKD-iPSCs derived neurons. (A) Cells were held at −70 mV, and inward sodium currents were elicited by voltage steps from −70 to +30 mV in 10 mV increments for CON (red) and PKD (blue) iPS derived neurons. (B) Current injection-induced action potential of both CON- and PKD-iPSC-induced neurons. (C) Representative traces show systematic increase in IA generated by the hyperpolarizing prepulses. (D) Both CON- and PKD-iPSC-induced neurons could generate sodium current using the same pulse protocol as in A. (E) Statistical analysis of C. The IA currents showed no differences between CON- and PKD-iPSC-induced neurons when normalized to the peak current. To test whether different path voltage will influence the IA current between the two groups two-way ANOVA was used for the data analysis. (F) Statistical analysis of D. No significant difference was detected of the fast activated and deactivated sodium currents between the CON- and PKD-iPSC-induced neurons. Two-way ANOVA was used for the data analysis. Error bars represent s.e.m.