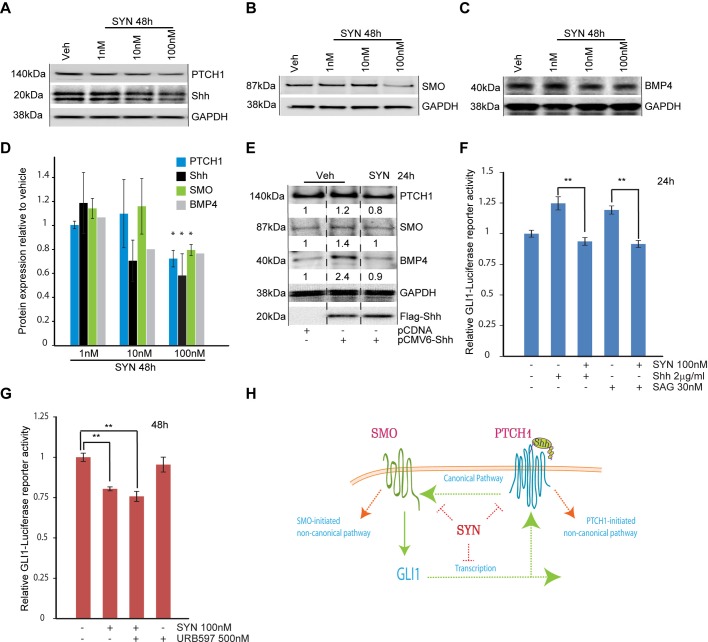
Fig. 3.
Synaptamide antagonizes sonic hedgehog signaling in cortical neurons. (A-C) Representative western blot analysis of the cortical neurons supplemented at DIV1 with indicated concentrations of synaptamide. Equal loading was evaluated by reprobing membranes for GAPDH. In A, Shh and Patched-1 were probed from the same membrane. In B and C SMO and BMP4 expression levels were evaluated after synaptamide treatment at the indicated concentrations. (D) Quantification of western blots presented in A-C. Error bars are ±s.e.m. Statistical significance for western blots was calculated using Student's t-test; *P<0.05 vs vehicle. (E) Synaptamide antagonizes Shh target gene expression in cortical neurons. Immediately after isolation, cortical neurons were electroporated with 0.5 µg pCMV6-Flag-Shh or an equal amount of pCDNA plasmids per 1×107 cells. At 24 h after plating, neurons were treated with 100 nM synaptamide as indicated. After 24 h of treatment, neurons were lysed and analyzed by western blotting for BMP4, PTCH1, Shh and GAPDH, a representative blot of the experiments that were repeated three times is shown. (F,G) Mouse cortical neurons were co-electroporated with a GLI1-luciferase reporter and β-galactosidase expressing plasmids (1 µg pTF-GLI1-Luc-reporter and 0.2 µg EF1aLacZ per 1×107 cells). After plating for 24 h, DIV1 transfected neurons were treated with synaptamide, Shh (2 µg/ml) or SAG (30 nM) and FAAH inhibitor URB597 (0.5 µM) as indicated. Luciferase activity was evaluated at either 24 or 48 h after treatment. In F and G data represents the average of at least three independent experiments performed in duplicates, error bars are ±s.e.m. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer post hoc tests; **P<0.01. (H) Synaptamide antagonizes Hedgehog signaling. Canonical Hedgehog signaling is triggered by transactivation of SMO by Shh-PTCH1 complex. This leads to GLI-mediated transcription and expression of canonical target genes, including PTCH1 itself. Two general types of non-canonical pathways could be designated in Hedgehog signaling. First, SMO- and GLI1-independent signaling initiated by PTCH1 and second, GLI1-independent signaling initiated by SMO. Synaptamide antagonizes Hedgehog signaling by downregulating the expression of key Hedgehog-related proteins, such as PTCH1, SMO and by inhibiting GLI1-mediated transcription.