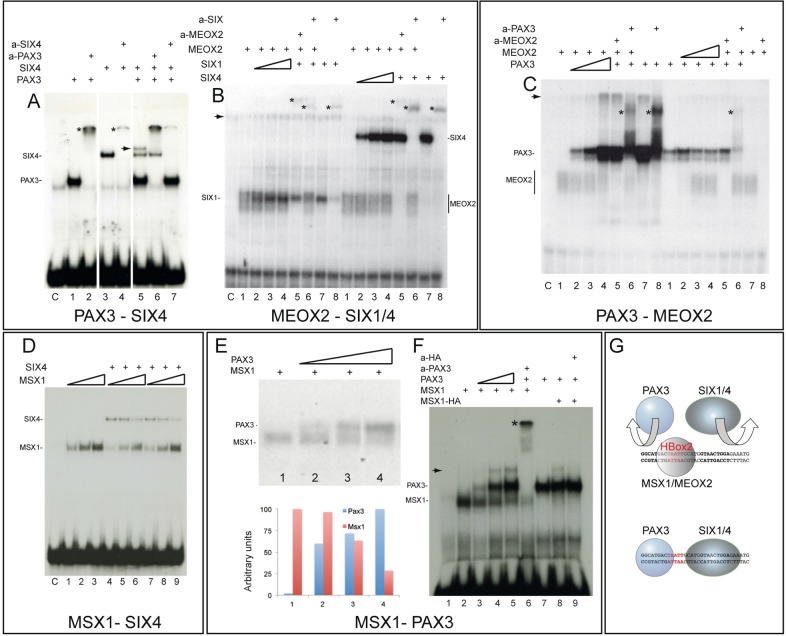
Fig. 2.
EMSA experiments with combinations of proteins to test co-binding or competition on the HBox2 probe. The labelled HBox2 probe, which contains Pax3 and Six binding sites was used in limiting molar amounts, compared to the proteins added. (A) Pax3 and Six4 proteins can bind together to the same DNA sequence. Pax3 binding (lane 1) is supershifted with anti-Pax3 antibodies (lane 2, asterisk). Six4 binding (lane 3) is supershifted when anti-Six4 antibodies are present (lane 4, asterisk). When both proteins are present, an additional slower migrating band is detected (lane 5, arrow) and the intensity of the band corresponding to Six4 binding alone is reduced, compared to lane 3. When anti-Pax3 (lane 6) or anti-Six4 (lane7) antibodies are added, this band, which is therefore due to co-binding of Pax3 and Six4 on the same oligo, is disrupted and the bands due to Pax3 or Six4 binding alone are supershifted. Similar results were obtained with Pax3 and Six1, with disruption of the Pax3/Six1 complex with anti-Pax3 antibodies (results not shown). Lane C is the control with crude lysate. (B) Meox2 and Six1/4 co-binding is not detectable. EMSA was performed with constant amounts of Meox2 and increasing amounts of either Six1 (left side of panel) or Six4 (right side of panel). Presence of anti-Meox2 (lanes 5) or anti-Six1 (left, lanes 6,8) or Six4 (right, lanes 6,8) antibodies are indicated above the panel. No additional slower migrating band, suggesting co-binding of Meox2 and Six proteins, is detected. A weak band (indicated by an arrow) was detected in most samples, including the control with crude lysate (lane C). Asterisks indicate the position of bands supershifted by antibodies. (C) Meox2 and Pax3 co-binding is not detectable. In the presence of constant amounts of Meox2 (left side of panel), no Pax3 (lane 1) or increasing amounts of Pax3 were added (lanes 2-4). No supplementary band is detected when both proteins are present. Controls are shown with Pax3 alone (lane 7) or with Pax3 and anti-Pax3 antibody (lane 8) or lysate alone (C). In the presence of constant amounts of Pax3 (right side of panel), no Meox2 (lane 1) or increasing amounts of Meox2 were added (lanes 2-4). No additional slower migrating band is detected when both proteins are present in the binding reaction. A weak band (arrow) was detected in most samples, including those without Meox2 and appears to represent a Pax3 complex with this lysate. Addition of anti-Meox2 (lanes 5, 8) or anti-Pax3 (lane 6) antibodies disrupt the bandshifts and, in the case of Pax3, generate a supershift (asterisk). Controls are shown with Meox2 alone (lane 7) or with Meox2 and anti-Meox2 antibody (lane 8). (D) Msx1 and Six4 co-binding is not detectable. Increasing amounts of Msx1 alone (lanes 1-3) or with constant amounts of Six4 added at the same time (lanes 4-6) do not produce an additional slower migrating band when both proteins are present. Six4 binding is reduced when higher amounts of Msx1 are added (lanes 4-6). This displacement occurs even if Six4 protein is added before Msx1 (lanes 7-9). (E) Msx1 binding is displaced by increasing amounts of Pax3. When constant amounts of Msx1 without (lane 1) or with 2.5, 5, or 10 fold amounts of Pax3 (lanes 1-4) are added, reduction of Msx1 binding is seen as Pax3 levels increase, under gel conditions which facilitate distinction of Pax3 and Msx1 binding with lower levels of Pax3. This is confirmed by the histogram showing a scan of this autoradiograph with ImageJ 1.47v. (F) Msx1 and Pax3 can bind together when the spacing between the sites is increased. One copy of a mutated HBox2* site, which does not bind Msx1 (see Fig. 4), was intercalated on either side of the bona fide HBox2 site, thus increasing the distance between Pax3 and Six binding sites. In the presence of constant amounts of Msx1 (lanes 2-6) and increasing amounts of Pax3 (lanes 3-5), a supplementary slower migrating complex appears (arrow). When anti-Pax3 antibody is added, this band disappears and Pax3 complexes are supershifted (asterisk, lane 6). This band does not appear if Pax3 is added alone (lane 7) but is detected when Pax3 and Msx1-HA proteins are added together or sequentially (lane 8) and disappears if anti-HA antibodies are added (lane 9). Note that bands corresponding to Pax3 or Msx1-HA complexes alone migrate at almost the same positions as shown in Fig. 1 (G) The drawing resumes the competition between homeoproteins such as Msx1 and Meox2 and Pax3/Six proteins for in vitro binding to the oligonucleotide probe in the EMSA experiments presented. The binding of a homeoprotein at the HBox2 site (red) prevents the binding of Pax3 or Six1/4.