Figure 4. HFAT feeding exacerbates the high fat diet induced liver injury in Arg2−/− mice.
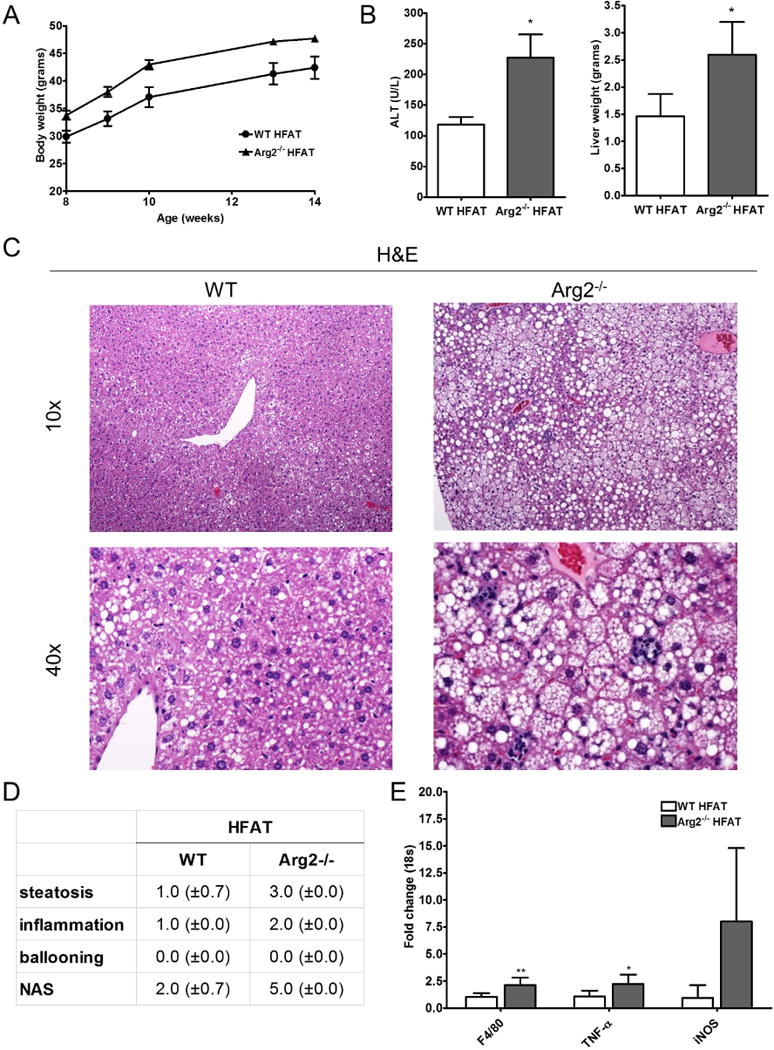
Within a short term feeding period with high fat (HFAT) diet for 6 weeks, Arg2−/− and WT animals gained significant weight (A). Livers of Arg2−/− mice weighed significantly more than those of WT mice after 6 weeks of high fat diet and ALT serum levels were significantly elevated in Arg2−/− mice on HFAT diet (B). Histological analysis of liver samples of revealed that Arg2−/− mice develop more steatosis than WT mice (C). More importantly, Arg2−/− mice showed increased lobular increased lobular inflammation which translated into an increase in the NAFLD-activity score (NAS). In line with this, global marker for macrophages (F4/80), as well as, markers for inflammatory macrophage polarization (TNF- α and iNOS) were increased in Arg2−/− mice when compared to WT mice on HFAT diet (E). Microphotographs are displayed in 10× and 40× magnifications. Mean ± S.E.M. are shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
