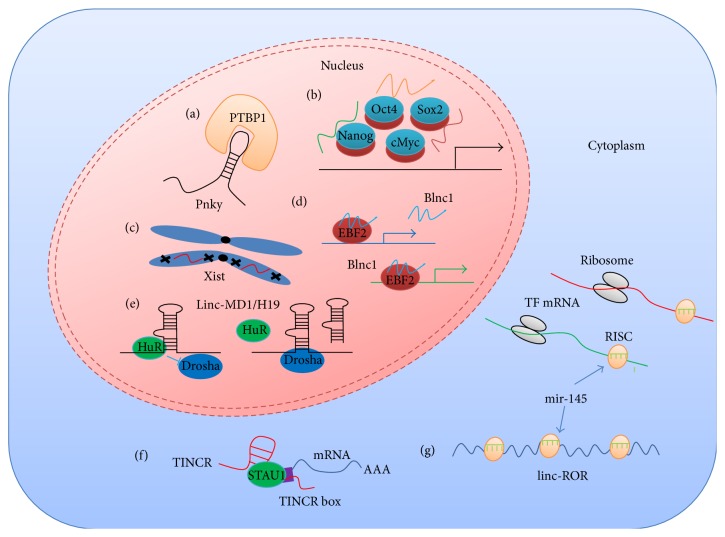
Figure 1.
Some known functional mechanisms of lncRNAs in stem cells. (a) Pnky localizes to the nucleus and interacts with the mRNA splicing regulator PTBP1 to regulate splicing of key transcripts; (b) some lncRNAs serve as cofactors of key transcription factors (TF) to regulate gene transcription; (c) Xist as an epigenetic regulator of X chromosome inactivation plays roles in female ESCs and iPSCs; (d) Blnc1 is activated by EBF2 and functions as a coactivator of EBF2; (e) linc-MD1 is the primary transcript of miR-133b and H19 is the primary transcript of miR-675, and the Drosha processing of both is regulated by HuR; (f) TINCR interacts with STAU1 and multiple mRNAs via an RNA motif called TINCR box; (g) linc-ROR functions as a mir-145 sponge.