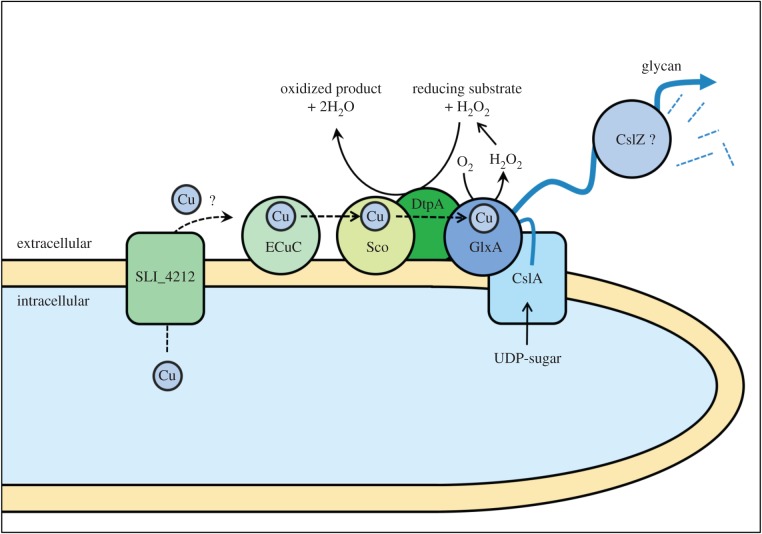
Figure 9.
Proposed model for the Cu-dependent morphogenesis pathway in hyphal tips of S. lividans. Mature GlxA requires the incorporation of a Cu ion and the formation of a Tyr–Cys covalent bond. GlxA receives its Cu from the extracellular chaperone Sco, which in turn receives Cu from the lipoprotein ECuC. The putative Cu transporter SLI_4212 may be involved in shuttling Cu ions over the membrane, although its activity is not essential for GlxA function. DtpA is required for maturation of GlxA, possibly by changing Cu(I) to Cu(II) before transfer from Sco to GlxA. DtpA probably also removes the reactive H2O2, which is generated by GlxA while oxidizing its substrate. Mature GlxA acts cooperatively with the cellulose synthase like protein CslA in formation of an extracellular glycan, which may be processed by the endoglucanase CslZ.