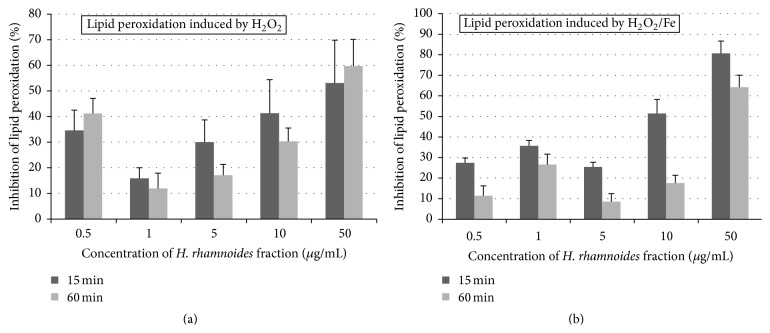
Figure 1.
Effects of the phenolic fraction from fruits of H. rhamnoides (0.5–50 µg/mL; 15 and 60 min) on plasma lipid peroxidation induced by H2O2 (a) and plasma lipid peroxidation induced by H2O2/Fe (b). Data represent means ± standard error (SE) of 4-5. The effect of five different concentrations of the tested fraction (0.5, 1, 5, 10, and 50 μg/mL) was statistically significant according to ANOVA I test, p < 0.05 for concentrations 0.5, 5, 10, and 50 μg/mL (for 15 and 60 min) (a); p > 0.05 for concentration 1 μg/mL (for 15 and 60 min) (a); p < 0.05 for concentrations 0.5, 1, and 5 μg/mL (for 15 min) (b); p < 0.02 for concentrations 10 and 50 μg/mL (for 15 min) (b); p < 0.02 for concentration 50 μg/mL (for 60 min) (b); p > 0.05 for concentrations 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 μg/mL (for 60 min) (b).