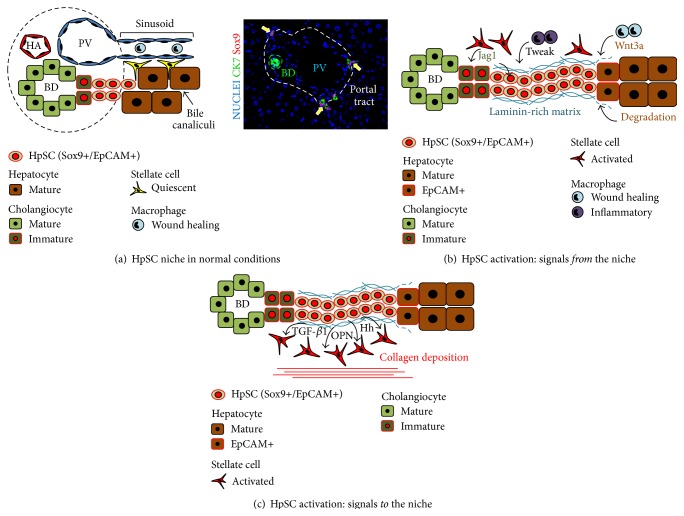
Figure 3.
Niche of hepatic stem/progenitor cells (HpSCs). (a) The cartoon shows the HpSC niche in adult liver. The HpSC niche is located within the smaller branches of biliary tree at the interface between portal tract and hepatic parenchyma. The niche is composed of the stem cells in combination with hepatic stellate cell precursors and Kupffer cells (resident macrophages). In the right side image, normal adult human liver: immunofluorescence for Sox9 and cytokeratin (CK) 7 (Original Magnification: 20x); CK7+/Sox9+ HpSCs (arrows) are present in canals of Hering and bile ductules. BD: bile duct; HA: hepatic artery; PV: portal vein. (b-c) Cartoons showing HpSC niche activation in liver diseases. (b) The HpSC response is surrounded by a specialized niche, composed of precursors to hepatic stellate and to endothelial cells and macrophages and of a matrix rich in laminin, hyaluronans, types III and IV collagens, and minimally sulfated proteoglycans. The microenvironment of such a niche maintains the stem/progenitor/biliary phenotype and inhibits hepatocyte differentiation; the transition of the niche matrix environment to one with minimal hyaluronans, less laminin, and an increase in more highly sulfated proteoglycans is a necessary step to start the differentiation into a hepatocyte (or cholangiocyte) phenotype. Cells of mesenchymal origin and macrophages can produce a variety of signals able to drive HpSC responses. Inflammatory macrophages can secrete TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) sustaining the expansion of undifferentiated HpSCs; contrarily, tissue-repairing macrophages are able to activate canonical Wnt pathway in HpSCs, triggering their differentiation towards hepatocytes. Activated hepatic stellate cells can secrete Jagged1, thus activating Notch signaling in HpSCs, and also release type I collagen promoting biliary specification. (c) Cartoon showing the profibrogenic loop induced by HpSC activation. HpSCs could activate the liver MF pool via Hedgehog (Hh) pathway, Osteopontin (OPN), and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), thus inducing collagen-I deposition.