Figure 6.
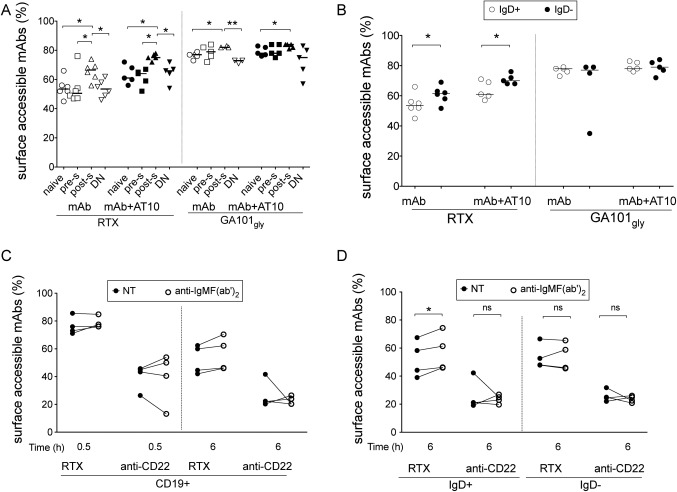
Effect of IgD and B cell activation on the internalization of anti‐CD20 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) in B cell subpopulations. A, Rituximab (RTX) was internalized to a significantly lesser extent by postswitched (post‐s) memory cells (IgD–CD27+) than by the other B cell subpopulations, both before and after blocking with AT10. A significantly greater percentage of glycosylated GA101 with an unmodified Fc portion (GA101Gly) was accessible on postswitched cells than on naive (IgD+CD27–) or double‐negative (DN; IgD–CD27–) cells before blocking with AT10 and only on naive cells after blocking with AT10. Preswitched (pre‐s) cells were defined as IgD+CD27+ B cells. B, A greater percentage of RTX was accessible on the surface of IgD– B cells than on IgD+ B cells. No such difference was noted for GA101Gly. C, Internalization of RTX was not inhibited by B cell activation with anti–IgM F(ab′)2 in CD19+ B cells as compared with no treatment (NT). D, A greater percentage of RTX was accessible at 6 hours in IgD+ B cells, but not IgD– B cells, from samples incubated with anti‐IgM F(ab′)2 as compared with untreated samples. No such difference was noted for anti‐CD22 mAb. In A and B, each symbol represents an individual sample; horizontal lines show the median. In C and D, each line represents an individual sample. ∗ = P < 0.05; ∗∗ = P < 0.005. NS = not significant.
