Figure 3.
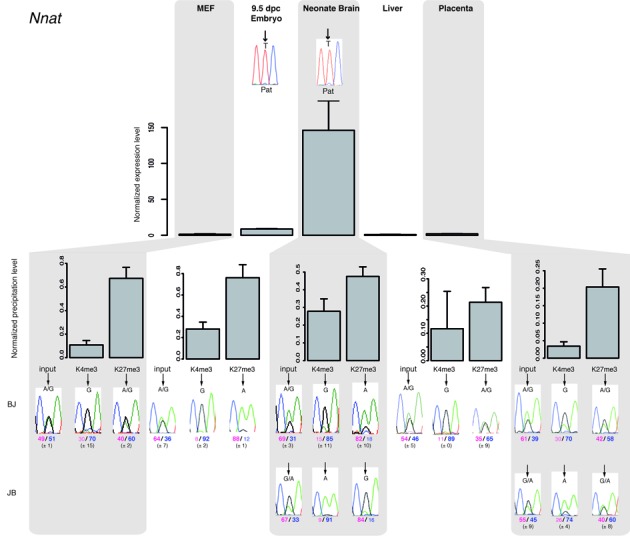
Paternal gene expression correlates with loss of H3K27me3 on the paternal allele at bivalent chromatin-associated ICRs. The upper panel shows representative results of gene expression in MEFs, embryos and tissues from BJ mice. Results were normalized to the expression level of the two housekeeping genes Ppia and Rpl30. Experiments were repeated four times, each in duplicate. The parental origin of gene expression was determined by direct sequencing of the PCR product encompassing a strain-specific SNP in the analyzed region. Lower panels: chromatin analysis following native ChIP using anti-H3-K4me3 and -K27me3 antibodies in BJ and JB (for neonate brain and placenta) samples. The precipitation level was normalized to that obtained at the Rpl30 promoter (for H3K4me3) and at the HoxA3 or HoxD8 promoter (for H3K27me3). The allelic distribution of each mark was determined by direct sequencing of the PCR product encompassing a strain-specific SNP in the analyzed region. The mean values (± standard deviation) of the relative allelic ratios (Pink: maternal; Blue: paternal) are indicated under representative chromatograms. For each tissue, values are the mean of at least three independent ChIP experiments (n), each in duplicate: MEFs (n = 3); E9.5 embryos (n = 3); neonate brain (BJ n = 2; JB n = 2); liver (n = 3); placenta (BJ n = 2; JB n = 1).
