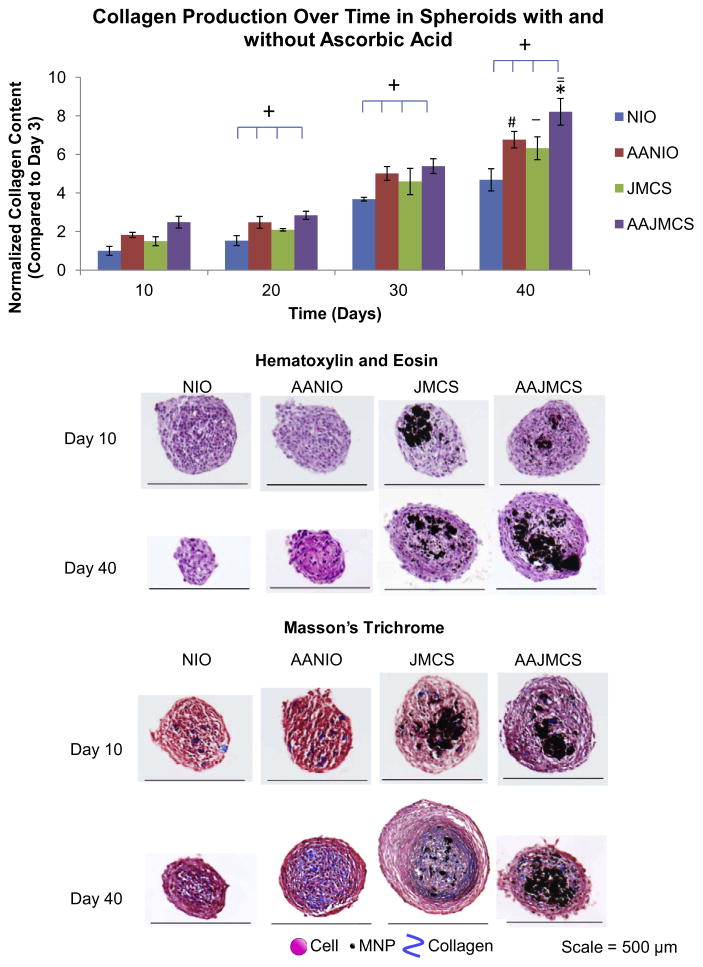
Fig. 1.
Effect of iron oxide MNPs on collagen synthesis within JMCSs. Results of hydroxyproline assays qualitatively demonstrate increased collagen production in NIO, AANIO, JMCS and AAJMCS spheroids over 40 days (P < 0.05, as indicated by “+”). Results demonstrated that the addition of iron oxide MNPs in JMCSs caused a significant increase in collagen production, when compared to their NIO counterparts (P < 0.05, as indicated by “_”). Further, the addition of ascorbic acid significantly increased ECM production of both spheroid types (P < 0.05, as indicated by “#” for NIO and AANIO and “*” for JMCS and AAJMCS groups). It should be noted that the combination of Janus spheroids with ascorbic acid had a synergistic effect, as the collagen content in these spheroids was significantly greater than in spheroids with ascorbic acid supplementation and no MNPs (P < 0.05, as indicated by “=“). Results of the Masson’s Trichrome stain suggest that all spheroid samples secrete their own collagen over time (increase in blue), which indicates that MNPs have no adverse effects on collagen synthesis within cellular spheroids. NIO = no iron oxide, AANIO = ascorbic acid no iron oxide, JIO = Janus iron oxide, AAJIO = ascorbic acid Janus iron oxide.