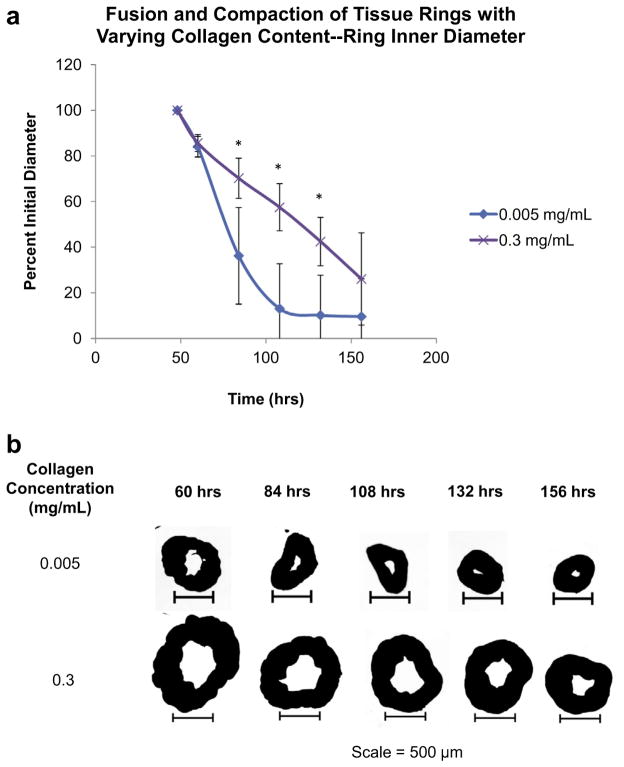
Fig. 4.
Effects of ECM on ring fusion and compaction. The effects of varying collagen contents for tissue fusion and compaction was quantified over time for rings composed of JMCSs with two collagen contents, 0.005 mg ml− 1 and 0.3 mg ml− 1. (a) At the 84 h, 108 h and 132 h time points the percent initial ring diameters of the 0.005 mg ml− 1 collagen spheroids were significantly smaller when compared to the 0.3 mg ml− 1 collagen spheroid counterparts (P < 0.05, as indicated by “*”). Four measurements for each ring diameter were recorded (vertical, horizontal and two diagonals) and averaged at each time point. (b) Visual analysis of ring fusion confirms that collagen content plays a significant role in tissue fusion and compaction, with decreases in fusion and compaction becoming evident with increasing collagen concentrations.