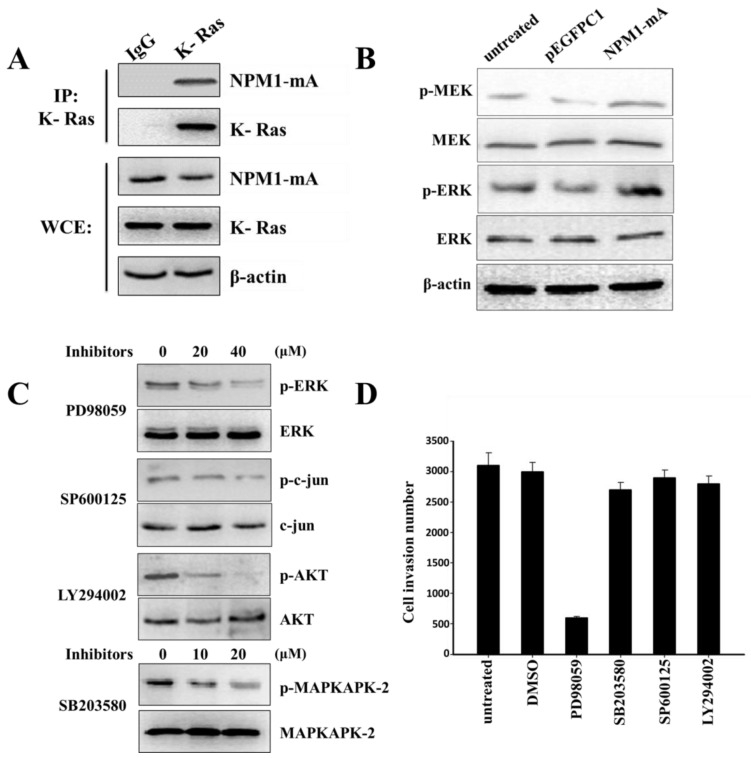
Fig 4.
The Ras/ERK MAPK pathway was involved in the invasion of THP-1 cells with NPM1-mA overexpression. (A) The NPM1-mA interaction with K-Ras was determined by an immunoprecipitation assay with THP-1 cells that ectopically expressed NPM1-mA. There was a clear band in the K-Ras group, but not in the negative control group (IgG group). The experiments were repeated three times, and a representative blot is shown. (B) Western blotting showed that NPM1-mA overexpression increased the MEK and ERK phosphorylation levels. (C) Western blotting results showed a dose-dependent reduction of p-ERK by the ERK/MAPK inhibitor, PD98059, a reduction of p-c-jun by the JNK/MAPK inhibitor, SP600125, a reduction of p-AKT by the PI3-K/AKT inhibitor, LY294002 and a reduction of p-MAPKAPK-2 by the p38/MAPK inhibitor, SB203580. (D) Cell invasion was tested after THP-1 cells with NPM1-mA were treated with PD98059 (40 µM), SB203580 (20 µM), SP600125 (40 µM), LY294002 (20 µM). The DMSO group, the solvent that was used for these inhibitors, and an untreated group were used a controls in this experiment. The cell invasion numbers were significantly decreased in the cell group that was treated with PD98059 (p<0.01). Data are expressed as the means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. **p<0.01 vs. control.