Figure 7.
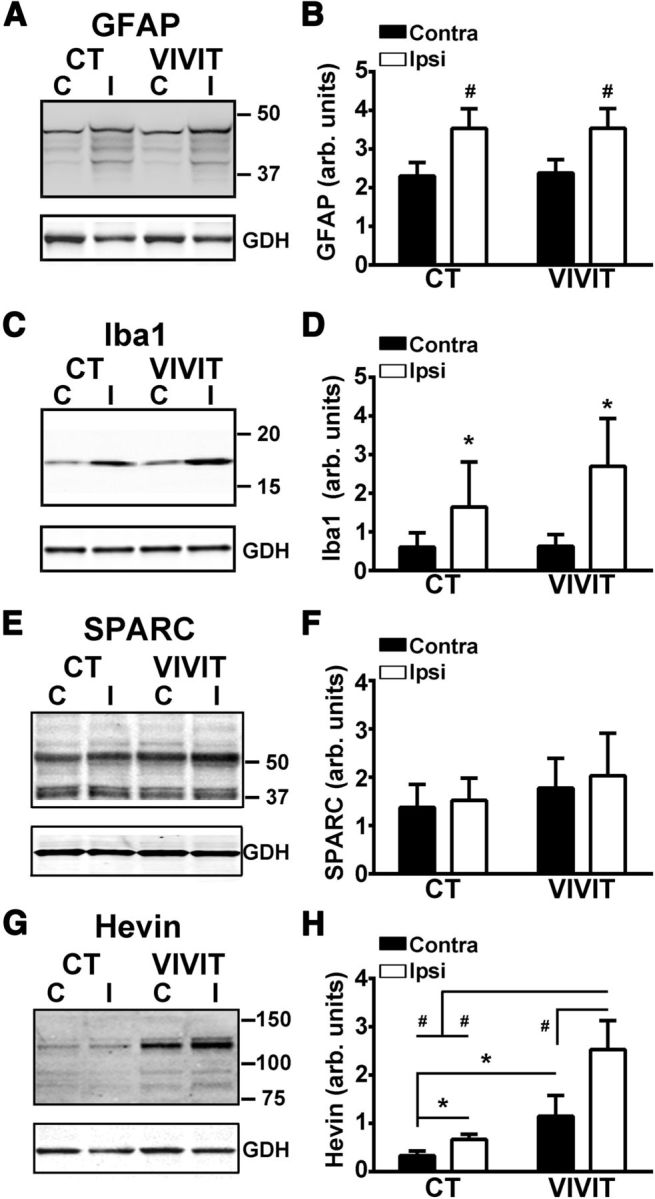
AAV-Gfa2-VIVIT does not alter GFAP or Iba1 levels, but causes an increase in hevin levels. Representative Western blots (A, C) and mean ± SD. GFAP and Iba1 protein levels (B, D) in the contralateral and ipsilateral hippocampus of AAV-treated rats at 7 d after CCI. Note that both glial markers showed a significant increase in the hippocampus of the ipsilateral hemisphere, but were not significantly altered by pretreatment with AAV-Gfa2-VIVIT. #p < 0.001 ipsilateral versus contralateral, Fisher's PLSD. n = 5–6 rats, group. E–H, Representative Western blots (E, G) and mean ± SD SPARC and hevin protein levels (F, H) in the contralateral and ipsilateral hippocampus of AAV-treated rats at 7 d after CCI. No virus or injury-dependent effects were observed for SPARC. In contrast, hevin was sensitive to both injury and AAV treatment. In both AAV groups, hevin was elevated in the ipsilateral relative to the contralateral hemisphere. Overall hevin levels were greater in the VIVIT-treated group regardless of hemisphere, but were highest in the injured hemisphere. *p < 0.05; #p < 0.001 ipsilateral versus contralateral, Fisher's LSD, n = 5–6 rats.
