Figure 5.
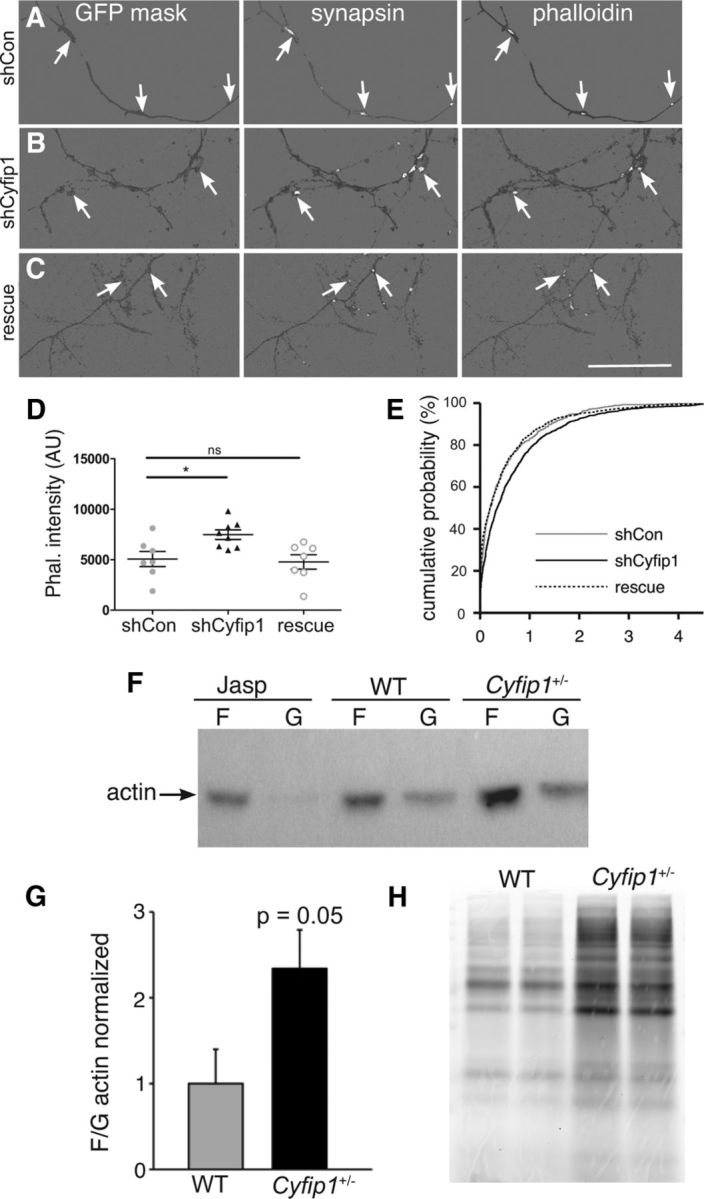
Presynaptic Cyfip1 regulates actin polymerization. A–C, Images of 10 DIV neurons expressing shCon, shCyfip1, or shCyfip1 + hCyfip1 together (rescue), immunolabeled for GFP and synapsin I, and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. A mask of GFP labeling (dark gray) was used to demarcate axons; synapsin and phalloidin labeling (white) is shown within the mask. Background was lightened to make the labeling easier to see. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Scatter plot shows that intensity of rhodamine-phalloidin labeling at sites defined by presynaptic labeling is increased in axons expressing shCyfip1 compared with shCon or rescue (shCyfip1 + human Cyfip1 cotransfection) (mean ± SEM). p = 0.013 (ANOVA). E, Cumulative probability plot of presynaptic phalloidin-associated fluorescence in shCon (gray), shCyfip1 (black), and rescue (dotted). F, Western blots reveal higher F-/G-actin in Cyfip1+/− brain tissues in 1-week-old mice compared with WT; Jasplakinolide (Jasp)-treated hippocampal lysate served as a positive control. G, Quantification of F-/G-actin ratio in the hippocampus from 1- and 4-week-old WT and Cyfip1+/− mice (n = 10 mice/genotype). p = 0.05 (t test). H, Image of a gel from a metabolic labeling experiment in which newly synthesized proteins in primary cortical neurons cultured from Cyfip1+/− and WT littermates were labeled by a click chemistry reaction. *p< 0.05. ns, Not significant.
