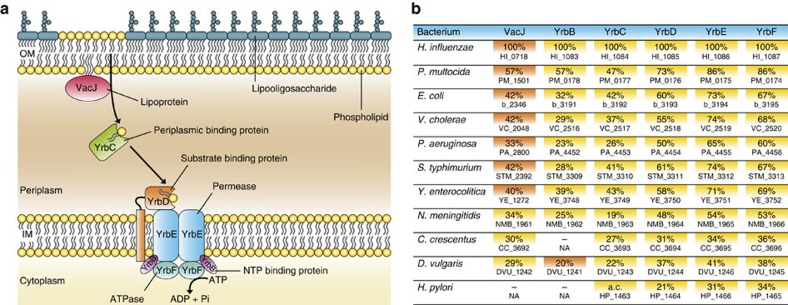
Figure 1. A conserved ABC transport system putatively prevents PL accumulation in the outer leaflet of the OM.
(a) The VacJ and Yrb proteins of H. influenzae are homologous to members of the E. coli Mla pathway, which has been proposed to maintain the lipid asymmetry in the Gram-negative OM by retrograde trafficking of PLs from the OM to the inner membrane (IM)24. The model is derived from the Mla pathway model proposed by Malinverni and Silhavy24. (b) Conservation of H. influenzae VacJ and Yrb proteins among Gram-negative bacteria. The respective genes or gene clusters were identified via the SSEARCH programme in combination with the SSDB (Similarity Sequence DataBase) using the KEGG database resource. Shown are the corresponding gene numbers and the respective amino acid sequence identities (in percentage), which were determined by BLASTp and/or Clustal Omega. Adjacent genes located in gene clusters are highlighted in yellow, genes located outside of the yrb gene clusters are coloured orange. In case of a single dash and NA (not applicable) no conserved homologous protein was identified. In Helicobacter pylori an auxiliary component (a.c.) with no homology to any other component is encoded within the yrb gene cluster. Genomes analysed were: H. influenzae Rd KW20 (γ), P. multocida Pm70 (γ), E. coli K-12 MG1655 (γ), V. cholerae O1 El Tor N16961 (γ), P. aeruginosa PAO1 (γ), Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 (γ), Yersinia enterocolitica 8081 (γ), N. meningitidis MC58 (β), Caulobacter crescentus CB15 (α), Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough (δ) and H. pylori 26695 (ɛ). The symbols α, β, γ, δ and ɛ refer to the class of the respective bacterium within the phylum Proteobacteria.