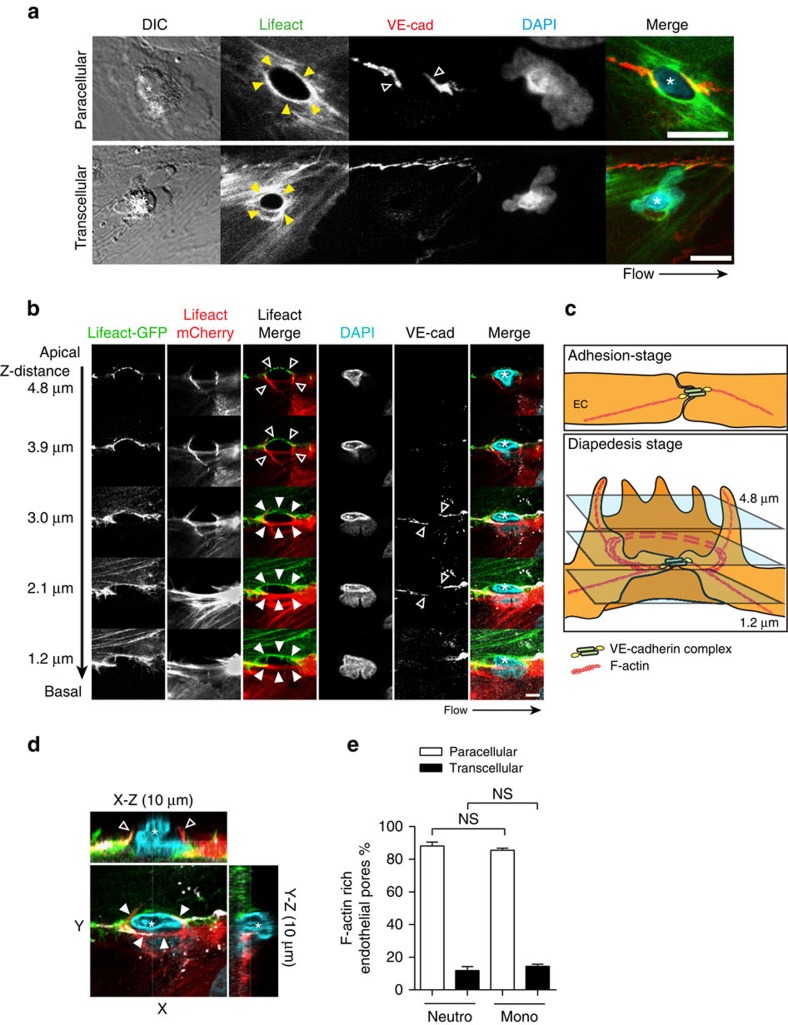
Figure 3. ECs assemble F-actin-rich ring-like structures around transmigrating leukocytes.
(a) Confocal imaging of para- and transcellular migrating leukocytes through Lifeact-GFP expressing HUVECs. Filled arrows indicate EC F-actin (Lifeact in green) assembly around extravasating leukocytes. Open arrows indicate VE-cadherin (directly labelled Alexa-647 antibody in red) distribution to the F-actin structure sites during paracellular diapedesis. Asterisks indicate extravasating leukocyte (DAPI in blue) in DIC. Flow speed 0.8 dyne per cm2. Scale bar, 5 μm. (b) Confocal imaging showing a Z-stack of Lifeact-GFP and Lifeact-mCherry positive endothelial membrane structures from apical to basal plane. Open arrows indicate filopodia-like protrusions at the apical site of the structure. Filled arrows indicate the cortical actin ring at the basolateral site that appeared during leukocyte crossing. Asterisk indicates extravasating leukocyte (DAPI in blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. (c) Cartoon of endothelium during basal-stage and leukocytes diapedesis showing filopodia-like protrusions and the basolateral F-actin ring. (d) X–Z (10 μm) and Y–Z (10 μm) projections of confocal Z-stack shown in Fig. 1b. (e) Quantification of percentage F-actin-rich endothelial pores associated with neutrophil and monocyte extravasation during para- and transcellular migration. Statistical significance was tested with ANOVA. Data are representative for three independent experiments (a–e) with 37–65 transmigration events per group (error bars (e) s.e.m).