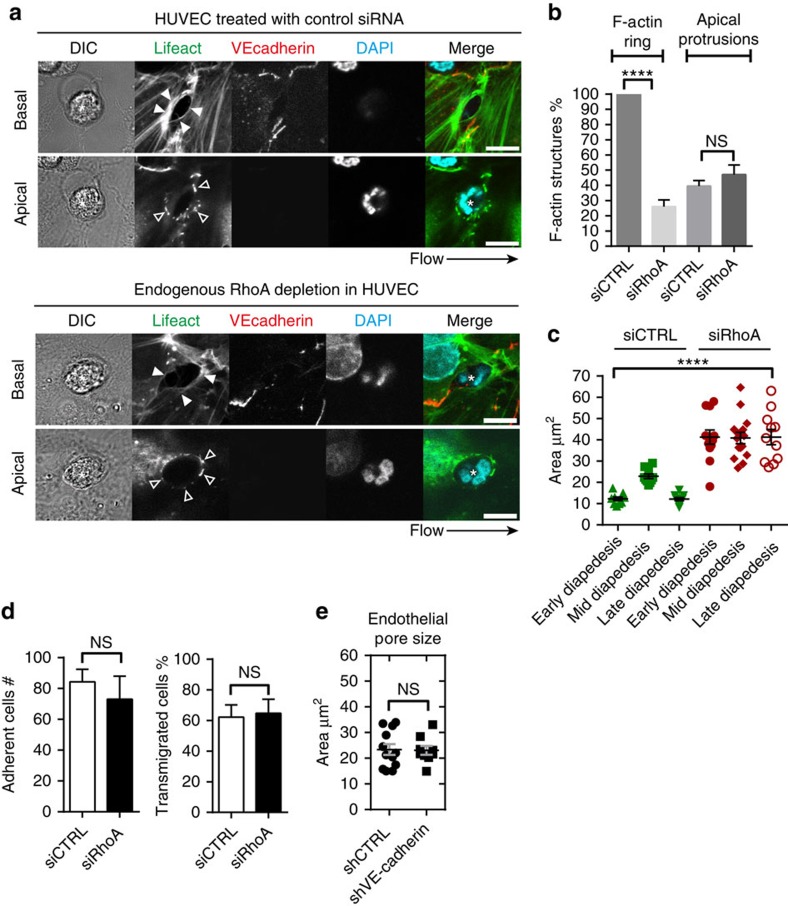
Figure 5. RhoA signalling is required for endothelial pore confinement.
(a) Confocal imaging of paracellular migrating neutrophils through Lifeact-GFP expressing HUVECs after 72-h transfection with control siRNA (upper panel) or RhoA siRNA (lower panel) under physiological flow conditions (0.8 dyne per cm2). Open arrows and filled arrows indicate filopodia-like protrusions at the apical site and the cortical F-actin ring at the basolateral site of the endothelial pore, respectively. Asterisk indicates extravasating neutrophil (DAPI in blue). VE-cadherin (red). Scale bar, 5 μm. (b) Quantification of F-actin-positive ring structures and F-actin-positive apical protrusions in control versus RhoA-depleted ECs. (c) Quantification of endothelial pore size during early, mid and late diapedesis. (d) Quantification of neutrophil adhesion and diapedesis through TNF-α treated ECs under physiological flow conditions after 72 h transfection with control siRNA (open bar) or RhoA siRNA (filled bar). (e) Quantification of endothelial pore size in control versus VE-cadherin depleted HUVECs. ****P<0.0001 (analysis of variance). Data are representative of four independent experiments (a–e) with >12 transmigration events per group (error bars (c,e) s.e.m).