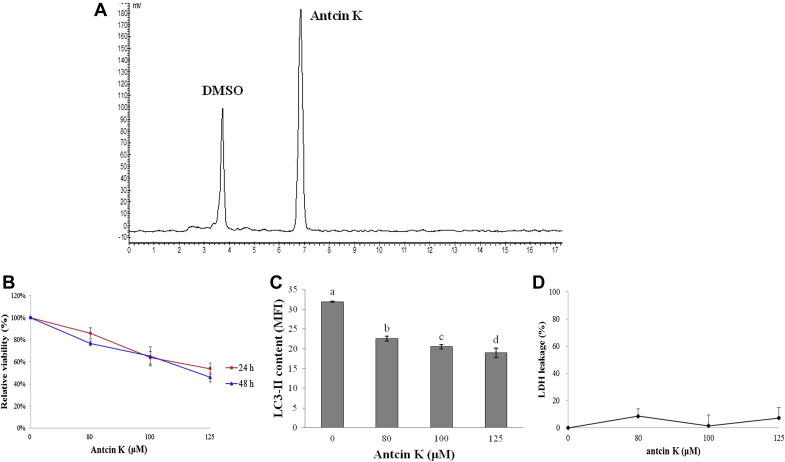
Fig. 1.
(A) High-performance chromatogram of the purified compound antcin K (retention time 6.5 minutes). Conditions: column, COSMOSIL 5C18-AR-II RP-C18; flow rate, 1 mL/min; detector, 254 nm; mobile phase, methanol (70%)/water (30%). (B) Effect of antcin K on cell viability in Hep 3B cells. After incubation of the cells with 0μM, 80μM, 100μM, and 125μM antcin K for 24 hours and 48 hours, cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data are expressed as percentage of negative control (0.2% DMSO) and mean ± SD from one of three independent experiments. (C) Effect of antcin K on the degree of LC3-II fluorescence intensity in Hep3B cells. After incubation of the cells with 0μM, 80μM, 100μM, and 125μM antcin K for 48 hours, the degree of LC3-II fluorescence intensity was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Effect of antcin K on degree of cell disruption in Hep 3B cells. After incubation of the cells with 0μM, 80μM, 100μM, and 125μM antcin K and lysis solution for 48 hours, the degree of cell disruption was determined by LDH leakage assay. Data are expressed as percentage between positive control (lysis solution) and negative control (0.2% DMSO) and mean ± SD from one of three independent experiments, and analyzed statistically using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's test. Different letters (a–d) represent statistically significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05). ANOVA = analysis of variance; DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide; LDH = lactate dehydrogenase; SD = standard deviation.