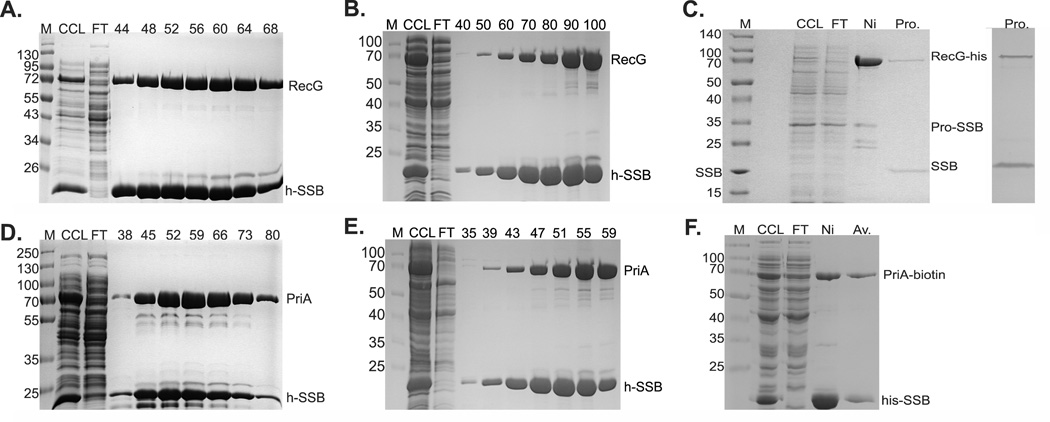
Figure 4. PriA and RecG bind to SSB in vivo.
1L cultures of cells expressing PriA and SSB, and separately, RecG and SSB were grown to early log phase, IPTG added to 200 µM and growth continued until early stationary phase. Cells were harvested by centrifugation, lysed and the cleared cell lysate applied to a 5ml nickel column as described in the Experimental Procedures. Proteins were then eluted using an imidazole gradient following extensive washing to remove unbound proteins. Aliquots from various fractions throughout the purification were subjected to electrophoresis. The resulting 12% SDS-PAGE gels of the purification of helicase-SSB complexes are presented. Panels (A) - (C), co-purification of RecG and SSB; panels (D) - (F), co-purification of PriA and SSB. In (A) and (D), purification was done with buffer containing 600mM NaCl. In panels (B) and (E), the [KCl] was 150 mM. Panel (C), purification of the his-RecG/profinity-SSB complex; left panel, protein gel stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue; right panel, protein gel stained with silver. Panel (F), purification of the his-SSB/PriA-biotin complex. The numbers at the top of lanes indicates fraction numbers from the peak in the corresponding elution profiles (Figure S4 in Supporting Information). M, molecular weight marker; CCL, clear cell lysate; FT, flow through. Ni, pooled fractions from the nickel column; Av, pooled fractions from the avidin column; Pro, complex eluted from the profinity eXact column.