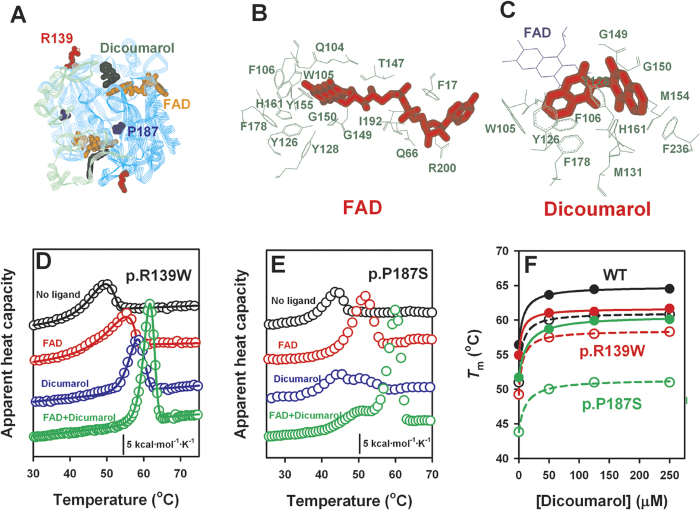
Figure 1. Dicoumarol and FAD mediated stabilization of NQO1 enzymes.
(A) Structural location of Arg139 (red) and Pro187 (blue) and the ligands FAD (orange) and dicoumarol (dark green) based on the ternary complex determined by X-ray diffraction (PDB: 2F1O35). The N-terminal domain (residues 2–217) and C-terminal domain (residues 218–274) are displayed in cyan and light green, respectively; (B,C) Binding sites of FAD (B; PDB: 1D4A36) and dicoumarol (C, PDB: 2F1O35), as determined by X-ray diffraction. (D,E) DSC profiles of R139W and P187S enzymes in the absence and presence of 100 μM FAD and 250 μM dicoumarol. Lines in panel (D) are fits to a two-state kinetic model. (F) Dicoumarol concentration dependence of Tm values for NQO1 enzymes in the absence (open symbols) and presence (closed symbols) of 100 μM FAD. For WT and p.R139W, Tm values are derived from fits to a two-state kinetic model, while for p.P187S correspond to the maximum of the heat capacity values for the high-temperature transition.