Abstract
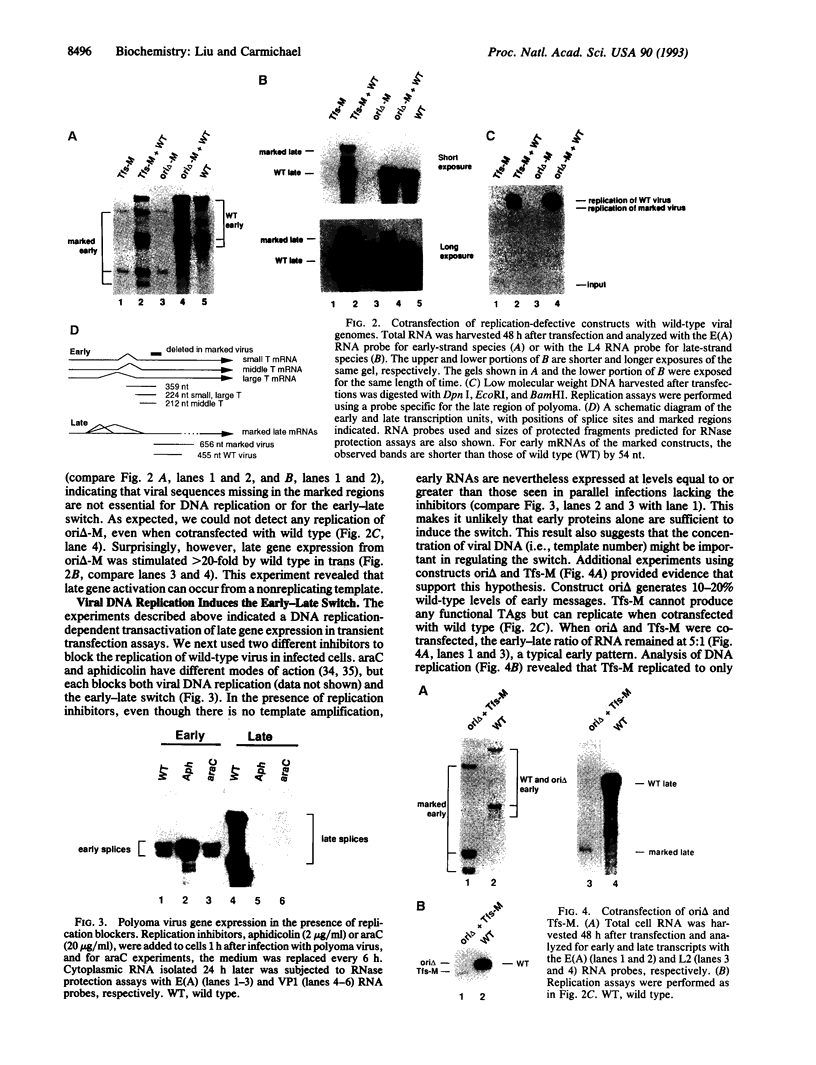
Early in infection of permissive mouse cells, messages from the early region of the polyoma virus genome accumulate preferentially over those from the late region. After initiation of DNA replication, the balance between early and late gene expression is reversed in favor of the late products. In previous work from our laboratory, we showed that viral early proteins do not activate the polyoma late promoter in the absence of DNA replication. Here we show that activation of the late genes in replication-incompetent viral genomes can occur if actively replicating genomes are present in the same cell. A low level of DNA replication, however, is insufficient to induce the early-late switch. Furthermore, replication-competent genomes that fail to accumulate late RNA molecules are defective in the transactivation of replication-incompetent genomes. We suggest that titration of an unknown diffusible factor(s) after DNA replication relieves the block to late RNA accumulation seen in the early phase, with most of this titration being attributable to late-strand RNA molecules themselves.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G. R., Marlor C. W., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Leader-to-leader splicing is required for efficient production and accumulation of polyomavirus late mRNAs. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.85-93.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G., Babiss L. E. DNA template effect on RNA splicing: two copies of the same gene in the same nucleus are processed differently. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3457–3465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Picardi J. Activity of simian virus 40 late promoter elements in the absence of large T antigen: evidence for repression of late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.400-404.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G., Luo Y. Splice site requirement for the efficient accumulation of polyoma virus late mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3011–3017. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Acheson N. H., Maxwell I. H. Strand-specific transcription of polyoma virus DNA-early in productive infection and in transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.20-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist A., Nilsson M., Bondeson K., Magnusson G. Loss of DNA-binding and new transcriptional trans-activation function in polyomavirus large T-antigen with mutation of zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2715–2720. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Roome A. J., Carmichael G. G. Replication-dependent transactivation of the polyomavirus late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):992–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.992-1001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catapano C. V., Perrino F. W., Fernandes D. J. Primer RNA chain termination induced by 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine 5'-triphosphate. A mechanism of DNA synthesis inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7179–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan J., Manley J. L. TFIID can be rate limiting in vivo for TATA-containing, but not TATA-lacking, RNA polymerase II promoters. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):304–315. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe J., Berger L., Smith D. B., Hehl R. K., Wildeman A. G. Activation of simian virus 40 transcription in vitro by T antigen. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4591–4596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4591-4596.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Multiple binding sites for polyomavirus large T antigen within regulatory sequences of polyomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):750–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.750-760.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Yamaguchi M., Possenti R., Bradley M. K., DePamphilis M. L. In vitro initiation of DNA replication in simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10863–10872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May P., Moreau P., May E. Simian virus 40 late promoter region able to initiate simian virus 40 early gene transcription in the absence of the simian virus 40 origin sequence. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.163-173.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Folk W. R. Regulation of polyomavirus transcription by large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Mandel G., Carmichael G. G., Barncastle J. P., Dawe C. J., Benjamin T. L. Polyomavirus tumor induction in mice: influences of viral coding and noncoding sequences on tumor profiles. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2232-2239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Chebli K., Himmelspach M., Stévenin J. Modulation of alternative splicing of adenoviral E1A transcripts: factors involved in the early-to-late transition. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1847–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grass D. S., Read D., Lewis E. D., Manley J. L. Cell- and promoter-specific activation of transcription by DNA replication. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1065–1074. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R. P., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing: DNA replication-associated changes in leader exon multiplicity suggest a role for leader-to-leader splicing in the early-late switch. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5823–5832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5823-5832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus early-late switch is not regulated at the level of transcription initiation and is associated with changes in RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8993–8997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierski W., Porter J. C. A novel non-enzymatic procedure for removing DNA template from RNA transcription mixtures. Biotechniques. 1991 Feb;10(2):210–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Bovi P. D., Basilico C. A reiterated leader sequence is present in polyomavirus late transcripts produced by a transformed rat cell line. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4055-4059.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Pellegrini S., Cowie A., Basilico C. Regulation of polyomavirus late promoter activity by viral early proteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):275–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.275-285.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Production of polyomavirus late mRNAs requires sequences near the 5' end of the leader but does not require leader-to-leader splicing. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4728–4734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4728-4734.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Simple, inexpensive preparation of T1/T2 ribonuclease suitable for use in RNase protection experiments. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):231–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Nilsson M. G., Magnusson G. Non-contiguous segments of the polyoma genome required in cis for DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M. Alternative mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:133–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. W. Polyoma virus transcription early during productive infection of mouse 3T6 cells. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Mueller C. R., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus large T antigen binds independently to multiple, unique regions on the viral genome. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):600–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.600-610.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P. Relationship of eukaryotic DNA replication to committed gene expression: general theory for gene control. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):512–542. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.512-542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo W., Martin M. E., Folk W. R. PEA1 and PEA3 enhancer elements are primary components of the polyomavirus late transcription initiator element. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5391–5400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5391-5400.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]