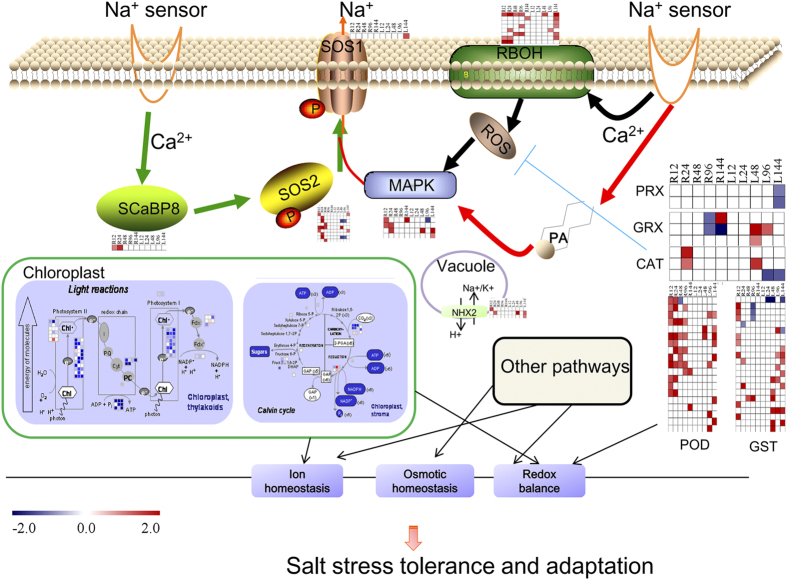
Figure 10. Model of the complex regulatory networks activated in response to salt stress in cotton.
Salt stress is first sensed by an unidentified mechanism. A Ca2+ spike generated in the cytoplasm activates the ROS (black route) and SOS (green route) pathways. In addition, photosynthetic pathways and metabolism in leaves (green boxes) were found to be changed to allow plants to adapt to osmotic and ionic stress at 96 h after salt stress. Meanwhile, other signaling methods such as hormones, and CDPK signaling factors, together alter the global transcriptional profile, resulting in gene expression and the activation of cellular detoxification mechanisms for ion homeostasis, osmotic homeostasis, and redox balance in plants. Transcription factors that were found to play important roles in SOS and ROS pathways are not displayed this figure. R12-R144 h and L12-L144 h indicate the different time points after salt stress in roots and leaves, respectively. Bar, log2 (fold change of DEGs).