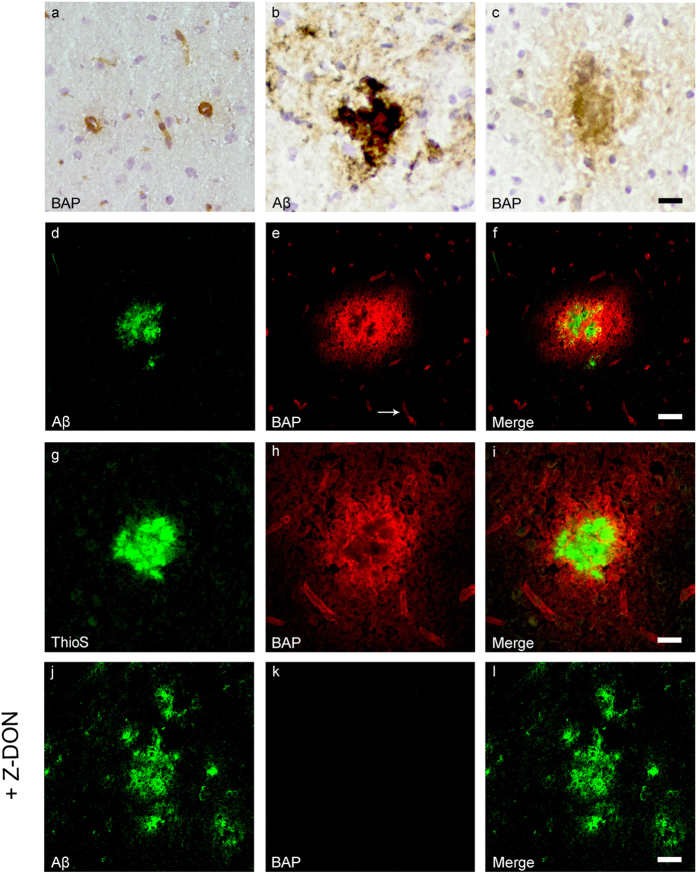
Figure 3. Distribution of in situ TG activity in C57Bl6/J wild-type and APP23 mice.
Serial sagittal whole brain sections of wild-type and APP23 mice were incubated with the TG substrate BAP or the anti-Aβ antibody and visualised using the DAB chromogen. The anti-Aβ antibody demonstrated Aβ plaques in 27-months old mice (b). BAP staining was found in the cerebral blood vessel walls of both 7-months old wild-type (a) and 27-months old APP23 mice (c). In addition, in APP23 mice BAP staining was present in Aβ plaque-like structures (c). Double immunofluorescence using the anti-Aβ antibody and BAP staining confirmed the presence of TG activity in Aβ plaques in 12-months old mice (d–f) as well as in cerebral vessel walls (e, arrow). BAP staining was found in the majority of dense core plaques, although it was absent from the cores of these plaques, confirmed by double immunofluorescence of ThioS with BAP (g–i). Co-incubation of BAP with the selective tTG inhibitor Z-DON (100 μM) blocked the tTG-catalysed incorporation of BAP (j–l). Scale bars: (c,d) 36 μm, (a,d–f,j–l) 30 μm, (g–i) 15 μm. Abbreviations: Aβ = amyloid beta, BAP = biotinylated 5-(biotinamido)-pentylamine, ThioS = Thioflavin S, tTG = tissue transglutaminase, Z-DON = Z-DON-Val-Pro-Leu-OMe.