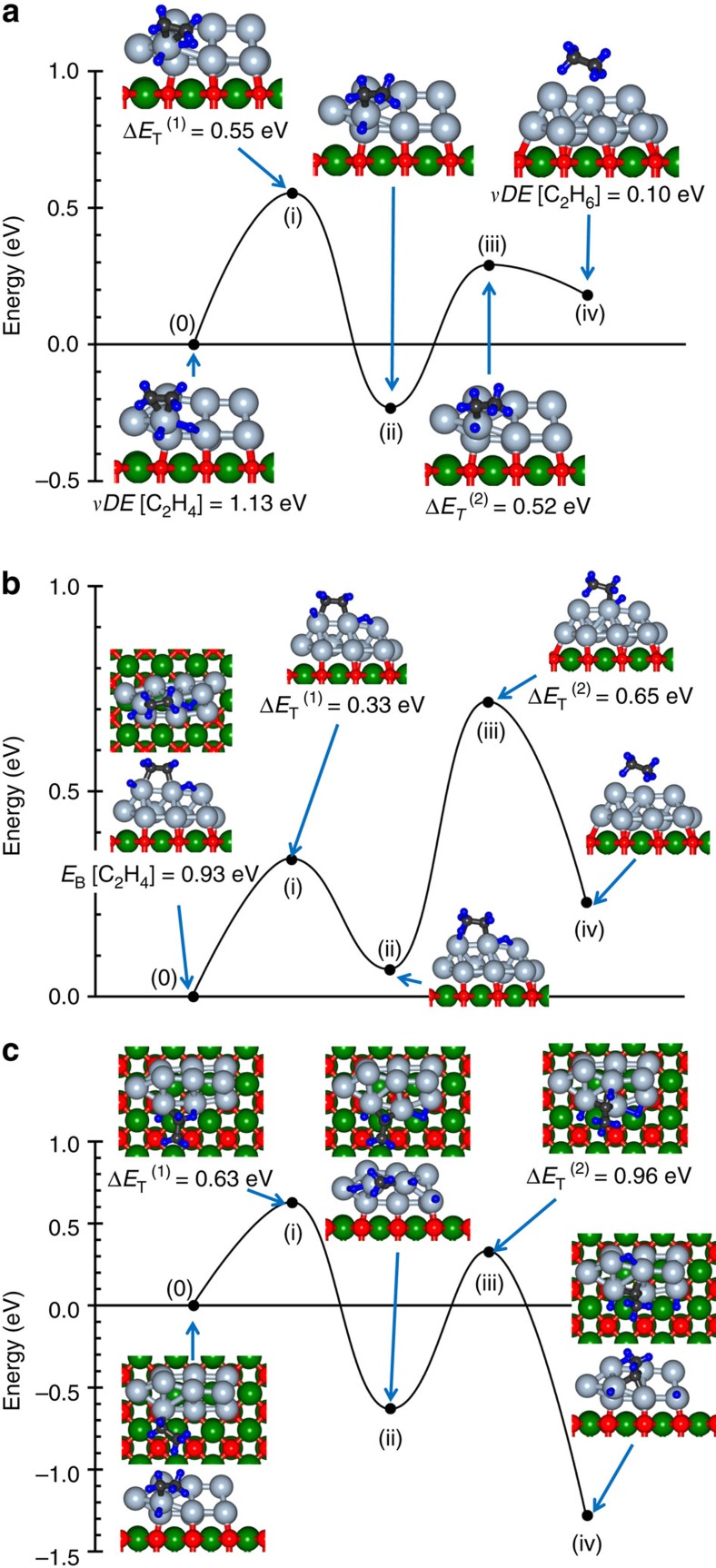
Figure 3. Calculated first-principles steered reaction pathways catalysed by Pt10/MgO.
(a,b) Low-activation-barrier reaction pathways for the π (a) and di-σ (b) bonded ethylene (configuration on the left, marked 0), co-adsorbed with dissociated hydrogen. The activation energy barriers are denoted as ΔET(k), k=1,2. The reaction proceeds through the two successive hydrogenation steps described in the Horiuti-Polanyi mechanism. (c) SRP for the low-temperature generation of ethylidyne (≡CCH3) on Pt10/MgO, starting from the ethyl (-CH2CH3) intermediate (configuration (0), on the left) generated in the first step of the reaction for the π-bonded ethylene (depicted as configuration (ii) in a). The two activation barriers correspond to dehydrogenation processes, resulting in a strongly adsorbed ethylidyne molecule (≡CCH3, configuration (iv)). Surmounting the barrier for the second dehydrogenation process is assisted by the highly exothermic (∼1.35 eV) formation of the -CHCH3 intermediate (iii) resulting from the first dehydrogenation step.