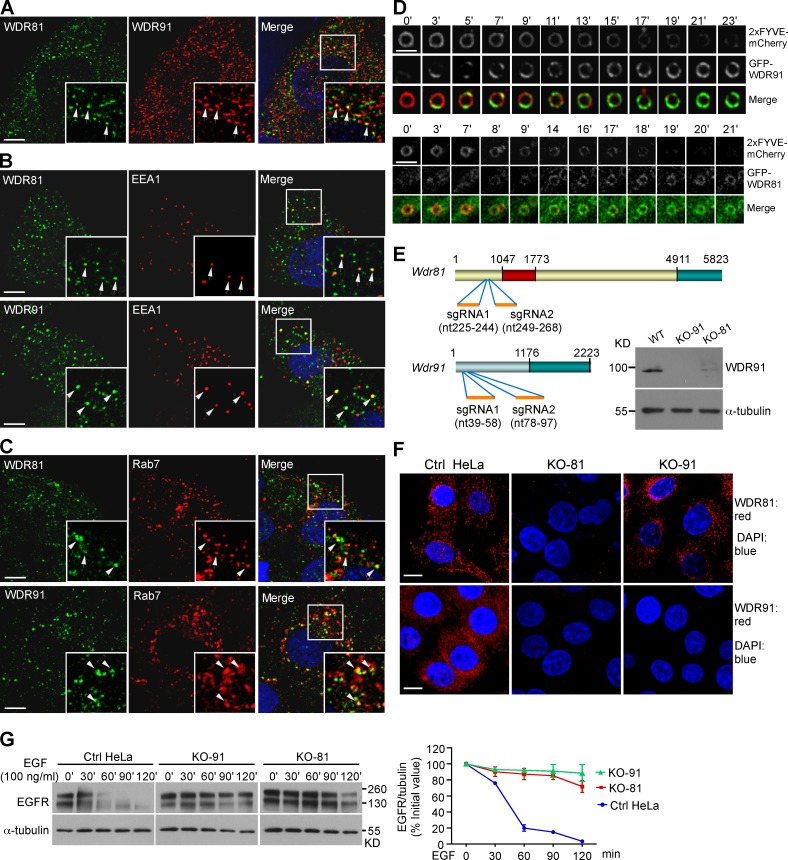
Figure 8.
Human WDR91 and WDR81 are recruited to endosomes and are important for endolysosomal trafficking. (A) Colocalization of WDR91 with WDR81 (arrows) in immunostained HeLa cells. Insets show magnified (1.8×) views of the box in the merged image. (B and C) Coimmunostaining of WDR91 or WDR81 with EEA1 (B) or Rab7 (C). Insets show magnified (1.8×) views of the boxes in the merged images. Arrows indicate colocalization of WDR91 or WDR81 with EEA1 or Rab7. Bars: (A–C) 5 µm. (D) Time course of 2xFYVE::mCherry and GFP-WDR91 (top) and GFP-WDR81 (bottom) on endosomes. Bars, 2 µm. (E) Top: sgRNA targeting sites in WDR81 and WDR91 cDNAs. Numbers indicate nucleotides (nt) starting from the first ATG. Bottom right: Western blot of WDR91 in control (Ctrl), WDR91 knockout (KO-91), and WDR81 knockout (KO-81) HeLa cells. (F) Immunostaining of WDR91 or WDR81 in Ctrl, KO-91, and KO-81 cells. Red, WDR91 or WDR81 antibody; blue, DAPI. Bars, 10 µm. (G) Ctrl, KO-91, and KO-81 cells were treated with EGF for 10 min, and then EGFR levels were examined by Western blot (left). EGFR levels were quantified with ImageJ software (right). Data representing mean ± SEM are from three independent experiments.