Figure 4.
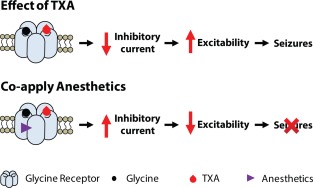
The molecular mechanism underlying tranexamic acid (TXA)‐associated seizures and the reversal of TXA‐mediated inhibition by anesthetics. TXA binds to the glycine receptors, resulting in a decrease in inhibitory current. This reduction in anion conduction increases excitability, which gives rise to seizures. Anesthetics reverse the effect of TXA by increasing glycine receptor function and thereby prevent or reverse TXA‐induced seizures.
