Figure 2.
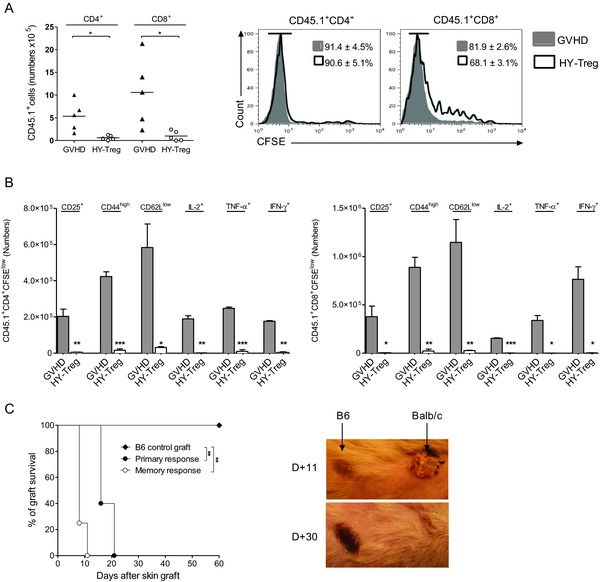
HY‐Treg cells prevent GVH disease by reducing activation and differentiation of donor Teff cells. Donor CD4+ and CD8+ Teff cells are analyzed at day 6 posttransplantation in the spleen of animals grafted as described in Fig. 1A and identified using the CD45.1+ congenic marker. (A) Mean absolute numbers and CFSE dilution of CD4+ and CD8+ donor CD45.1+ T cells when injected with or without HY‐Treg cells (n = 6 in each group). (B) Absolute numbers +SEM of CD4+ and CD8+ divided donor T cells (CD45.1+CFSElow) expressing membrane CD25, CD44, CD62L, or intracellular IL‐2, IFN‐γ, and TNF‐α with (white bars) or without (gray bars) HY‐Treg cells (n = 4 in each group). (C) Rejection of a third‐party allogeneic skin graft in mice protected from GVH disease with HY‐Treg cells. In order to evaluate the primary response of HY‐Treg cells protected mice, tail‐skin grafts from BALB/c mice were transplanted at day 60 onto the lateral thoracic wall (primary response, n = 6). On skin‐grafted mice, the memory response was tested by a second BALB/c skin grafted at day 150 (memory response, n = 5). Control group consists of mice treated with HY‐Treg cells and grafted with donor‐type B6 skin (B6 control, n = 5). Skin acceptance and rejection observed at days 11 and 30 in mice receiving a second skin graft is shown (right). Data shown are pooled from two experiments performed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test.
