Figure 5.
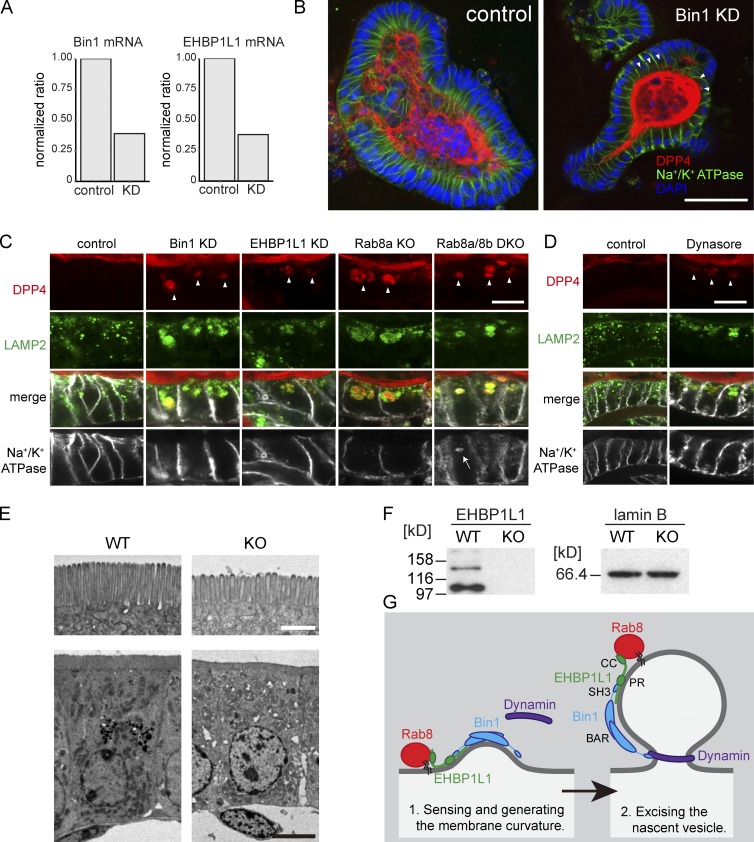
EHBP1L1 and Bin1 depletion induces the accumulation of apical but not basolateral membrane proteins in lysosomes. (A) EHBP1L1 and Bin1 mRNA levels in mouse small intestine organoids were analyzed using semiquantitative RT-PCR. The level of GAPDH mRNA was used for standardization. (B) Immunostaining for Na+/K+ ATPase (green) and DPP4 (red) in the mouse small intestine organoids. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The arrows indicate cytoplasmic DPP4 accumulation. Bar, 50 µm. (C) Magnified images of immunostaining for DPP4, Lamp2, and Na+/K+ ATPase in the small intestine Bin1 or EHBP1L1 KD organoids or organoids obtained from Rab8a or Rab8a/8b DKO mice. Arrowheads, DPP4 accumulation in lysosomes; arrow, Na+/K+ ATPase accumulation in lysosomes. Bar, 10 µm. (D) Immunostaining for DPP4 (red), Lamp2 (green), and Na+/K+ ATPase (white) in mouse small intestine organoids treated with DMSO (control) or 40 µM dynasore for 4 d. Bar, 10 µm. (E) Electron micrographs of epithelial cells in small intestines from EHBP1L1 KO mice and wild-type mice. Bars: (top) 1 µm; (bottom) 10 µm. (F) Immunoblot for intestine lysate from a WT or an EHBP1L1 KO mouse using an EHBP1L1 antibody. (G) Working model for Rab8, EHBP1L1, Bin1, and dynamin at the ERC. Bin1 is represented as a dimer (Owen et al., 1998).