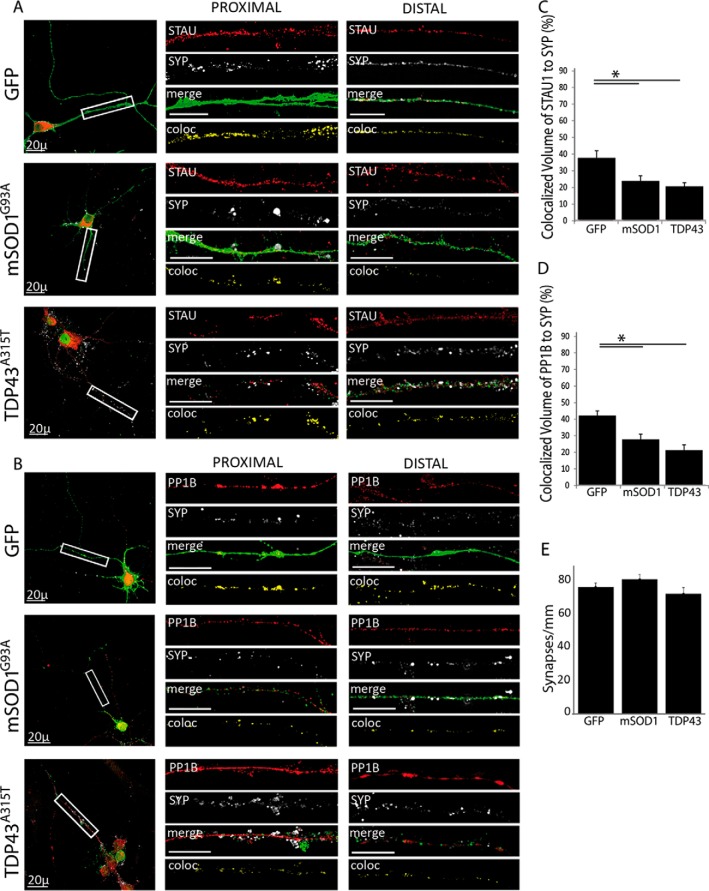
Fig. 8.
ALS-linked mutations decrease the association of STAU1 and PP1B with synaptic markers. Primary spinal cord neurons were seeded on cover slides and infected with lentiviruses expressing GFP, GFP-tagged mSOD1G93A, and TDP43A315T. After 10 DIV, cells were fixed and immunostained. Images were collected with a confocal microscope. Representative images of the neurons were taken with a 40x objective, with high-magnification close-ups of the proximal and distal axon taken with a 100x objective. High-magnification images were used to analyze volume colocalization along the neurites using the Imaris software, represented in the Coloc channel. The percentage of colocalized volume is shown. (A) Colocalization of SYP with STAU in infected neurons. (B) Colocalization of SYP with PP1B in infected neurons. (C) Quantification of SYP and STAU colocalization a ∼15% decrease in colocalized volume in ALS-infected neurons. (D) Quantification of SYP and PP1B colocalization showing a decrease of ∼15% in colocalized volume as a result of ALS-linked mutations. (E) The total number of synapses was quantified using the Image J software and normalized to neurite length. Statistical analysis was done with ANOVA, with Dunnet's post-hoc test, *p < .05. Unlabeled scale bars represent 10 μm, n = 3.