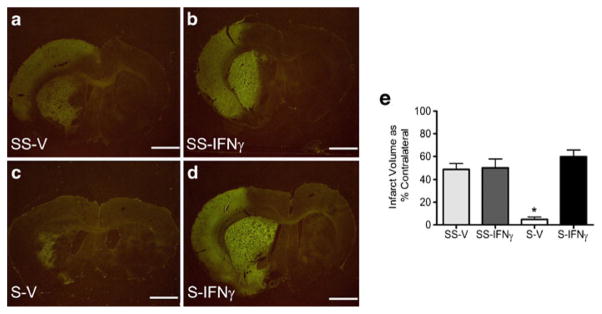
Fig. 5.
Recombinant IFNγ increases neural injury following MCAO in splenectomized rats. Recombinant IFNγ increases infarct volume in splenectomized rats at 96 h post-MCAO to levels not different from sham-splenectomized rats. Infarct volumes were measured as a percentage of the contralateral hemisphere with Fluoro-Jade staining. Graph depicts average infarct volumes for each group at 96 h post-MCAO (e). The splenectomy-vehicle treated rats had significantly lower infarcts than the other treatment groups (* p<0.0001). The splenectomy-IFNγ treated rats had infarcts that were not significantly different from the sham-splenectomy groups. Representative images for each treatment group at 96 h post-MCAO: sham-splenectomy-vehicle (SS-V) n=4 (a), sham-splenectomy-rIFNγ (SS-IFNγ) n=6 (b), splenectomy-vehicle (S-V) n= 4 (c), and splenectomy-rIFNγ (S-IFNγ) n=6 (d). Scale bars=2 mm