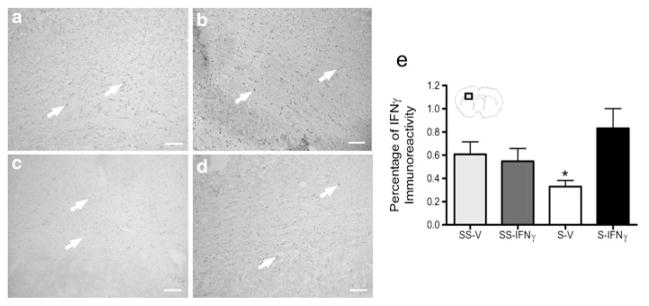
Fig. 6.
Recombinant IFNγ increases IFNγ expression in the infarct of splenectomized rats. The graph shows splenectomy results in a significant decrease in IFNγ protein expression at 96 h post-MCAO (* p< 0.02) (e). However rats that received splenectomy and rIFNγ had IFNγ protein levels not significantly different than the rats which underwent sham-splenectomy prior to MCAO. Representative images from each treatment group at 96 h following MCAO: sham-splenectomy-vehicle (SS-V) (a), sham-splenectomy-rIFNγ (SS-IFNγ) (b), splenectomy-vehicle (S-V) (c), and splenectomy-rIFNγ (S-IFNγ) (d). Box in brain graphics depicts the regions where images were taken for a given micrograph