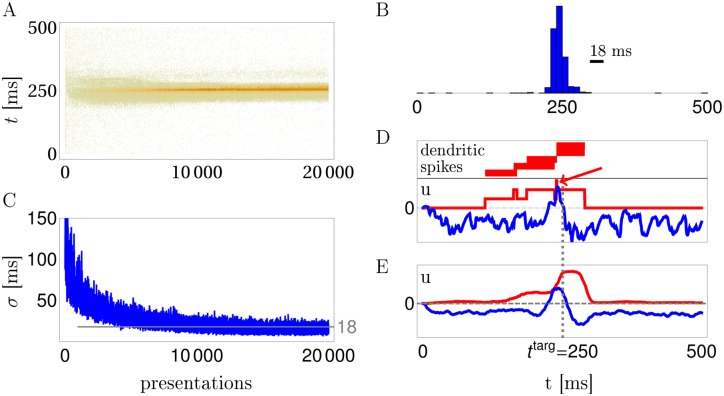
Fig 4. R-sdSP learns exact somatic spike timing.
A: Somatic spike trains during 20000 trials in a reward based scenario. B: The distribution of somatic spikes after learning of the target time at 250 ms has a Gaussian half-width of 18 ms. C: Evolution of the width (σ) of the spike-time distribution during training. D,E: Separation of the somatic voltage into a contribution from the NMDA-spikes (red) and the subthreshold dendritic potentials (blue) for a single run (D) and averaged across 20 runs (E). Note that after learning the summed NMDA-spikes can form a narrow depolarizations at the target time beyond the duration of an individual spike (arrow in D).