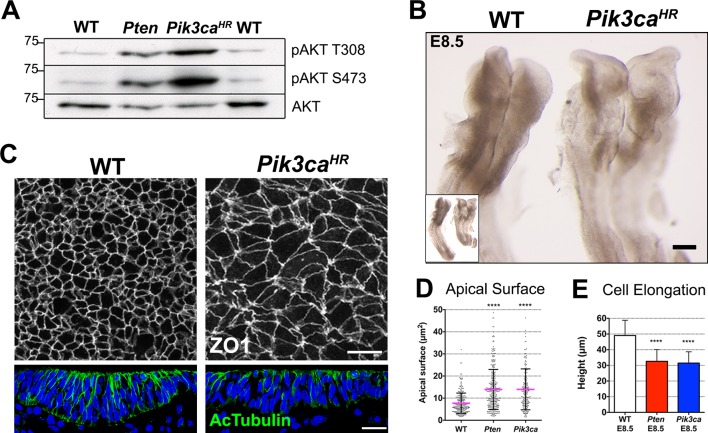
Figure 3. Expression of an activated form of PI3 Kinase mimics the Pten mutant neural plate phenotype.
(A) Loss of Pten (Pten △Epi) or expression of the activating mutation Pik3caH1047R-Epi in the epiblast leads to phosphorylation of AKT in E8.5 embryos. Representative Western blots (n = 3) show the two phosphorylated forms of AKT in WT, Pten △Epi and Pik3caH1047R–Epi embryos. Numbers indicate approximate MW. (B) Pik3caH1047R–Epi embryos phenocopy Pten △Epi embryos. Whole embryos (inset) and expanded view of the cephalic region of E8.5 WT and Pik3caH1047R-Epi embryos; dorsal view. Scale bar = 120 μm. (C) The apical surface of the neural plate, viewed en face; cell borders marked by expression of ZO1 (white) (top row), and acetylated tubulin (green) in transverse sections of the cephalic neural epithelium of E8.5 WT and Pik3caH1047R-Epi embryos. Blue is DAPI. Scale bar = 20 μm. (D) Comparison of apical surface area of cephalic neural epithelial cells at E8.5. WT = 8 ± 4 μm2; Pten △Epi = 14 ± 9 μm2; Pik3caH1047R-Epi = 15 ± 10 μm2. The surface areas of both mutants are significantly larger than wild type, ****p < 0.0001. (E) Cephalic neural plate height at E8.5. WT = 49.1 ± 9.6 μm; Pten △Epi = 32.6 ± 7.4 μm; Pik3caH1047R-Epi = 31.5 ± 7.2 μm. Cells in both mutants are significantly shorter than in wild type, ****p < 0.0001.