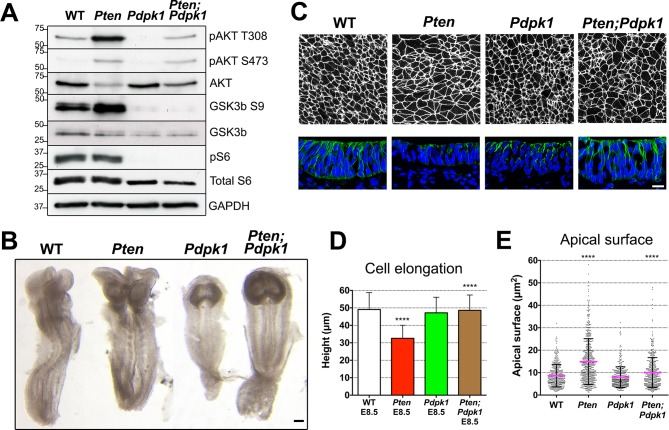
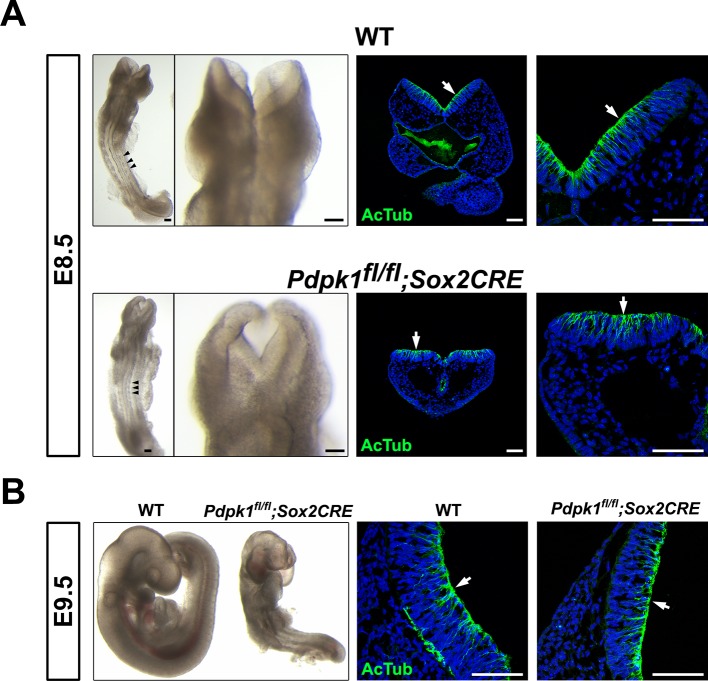
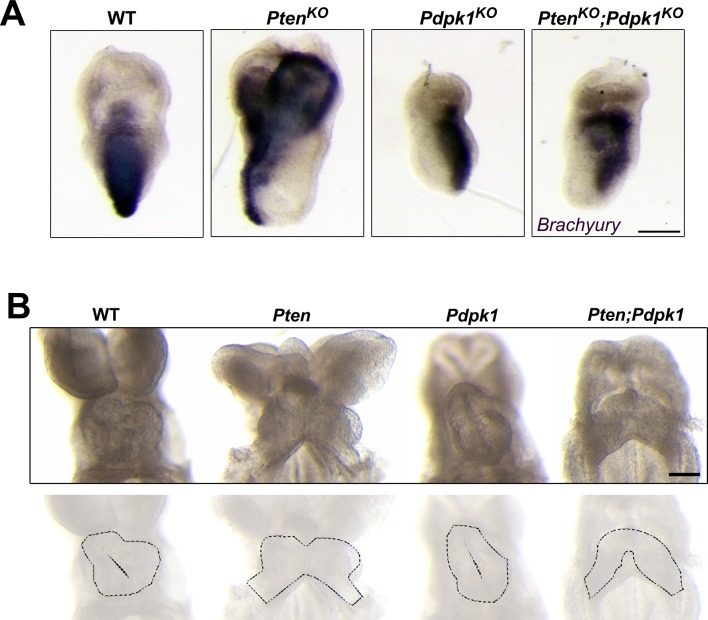
Figure 4. Removal of Pdpk1 rescues the pseudostratified columnar organization of the Pten neural plate.
(A) Phosphorylation of downstream targets of the PI3 kinase pathway in E8.5 wild type, Pten △Epi, Pdpk1 △Epi single mutant and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi double mutant embryos. Representative western blot shown (n = 3). Numbers indicate approximate MW. (B) Dorsal views of E8.5 wild-type, Pten △Epi, Pdpk1△Epi and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi embryos. The Pten Pdpk1 double mutants are similar in morphology to Pdpk1 single mutants, but are larger. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) The apical surface of the neural plate, viewed en face. Cell borders marked by expression of ZO1 (white) (top row) and acetylated tubulin (green) in transverse sections of cephalic neural epithelium in E8.5 wild-type, Pten △Epi, Pdpk1 △Epi and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi embryos. Blue is DAPI. Scale bar = 20 μm. (D) Cephalic neural plate height at E8.5. WT = 49.1 ± 9.6 μm; Pten △Epi = 32.6 ± 7.4 μm; Pdpk1 △Epi = 47.2 ± 8.9 μm; Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi = 48.6 ± 8.8 μm. Pten △Epi cells are significantly shorter than in wild type, and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi double mutant cells are significantly taller than in Pten △Epi, ****p < 0.0001. (E) Apical surface area of E8.5 cephalic neuroepithelial cells. Wild type = 9 ± 6 μm2; Pten △Epi = 15 ± 9 μm2. The surface area of Pten △Epi is significantly greater than in wild type, ****p < 0.0001; Pdpk1 △Epi = 8 ± 5 μm2; Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi = 10 ± 7 μm2; the surface area of Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi double mutant cells is significantly less than in Pten △Epi, ****p < 0.0001.