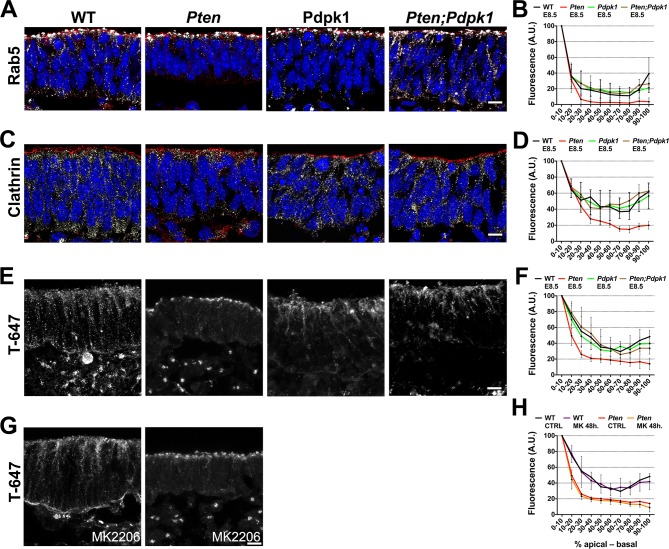
Figure 7. Apical-basal trafficking in PI3 kinase pathway mutants.
(A– D) Distribution of endosome markers along the apical-basal axis in transverse sections of the cephalic neural plate of E8.5 wild-type, Pten △Epi, Pdpk1 △Epi and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi embryos. (A) Localization of Rab5, an early endosome marker. (B) Distribution of Rab5 along the apical-basal axis, normalized to a maximum value of 100. (C) Localization of clathrin. (D) Distribution of clathrin along the apical-basal axis, normalized to a maximum value of 100. (E) Uptake of Transferrin-Alexa 647 after 8 hr of embryo culture. Transverse sections of cephalic neural plate of E8.5 wild-type, Pten △Epi, Pdpk1 △Epi and Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi embryos. White signal is the native Alexa 647 fluorescence. (F) Distribution of Alexa-647 signal along the apical-basal axis. Transferrin-647 accumulates apically in the Pten △Epi but not in Pten △Epi Pdpk1 △Epi double mutants. (G) Transverse sections of cephalic neural plate of E8.5 wild-type and Pten △Epiembryos treated in utero with MK-2206 for 48 hr and then cultured with 50 μg/ml of Transferrin-647 and MK-2206 for 8 hr. (H) Distribution of Alexa-647 along the apical-basal axis is not affected by MK-2206 treatment. Images are Z-projections of 3 optical sections of 1 μm each. Red is phalloidin. Blue is DAPI. Scale bars = 10 μm.