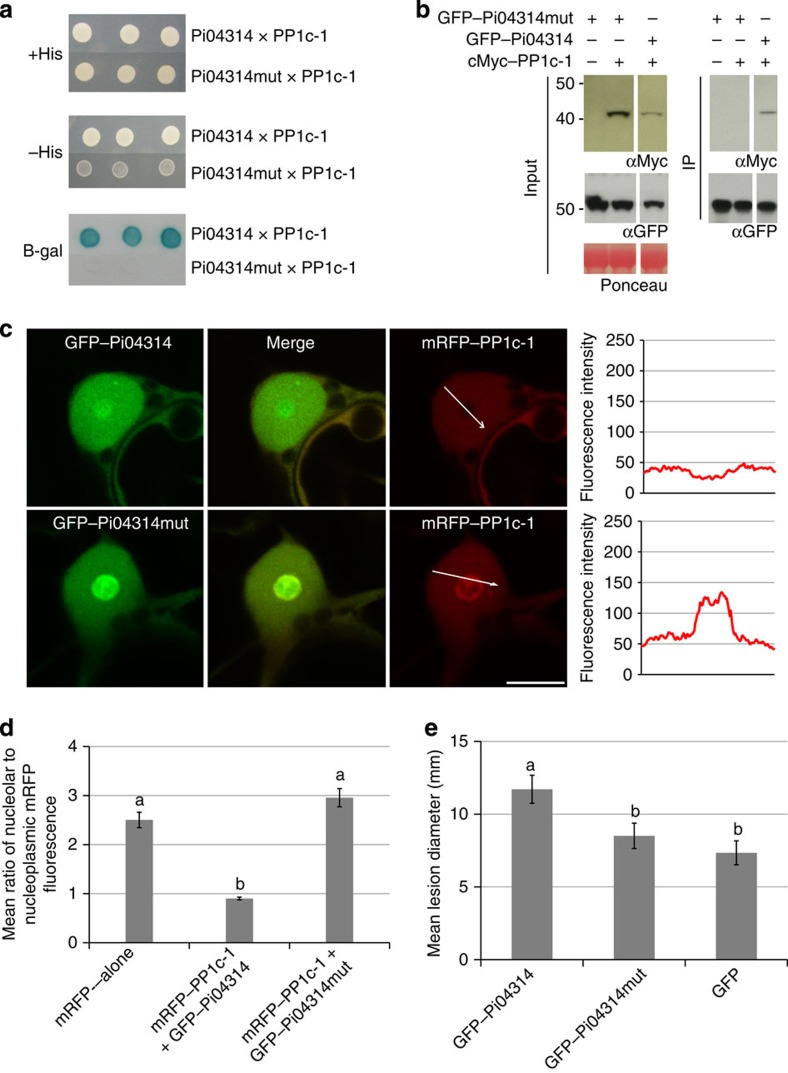
Figure 5. Mutation of the PP1c-binding motif in Pi04314 results in a loss of PP1c association.
(a) Yeast-2-hybrid assay following co-expression of PP1c-1 and wild-type (WT) Pi04314, which grew on −histidine (−HIS) medium and had β-galactosidase (B-gal) activity, while co-expression of PP1c-1 with Pi04314mut did not. (b) Immunoprecipitation of WT GFP–Pi04314 and GFP–Pi04314mut protein extracts from agroinfiltrated leaves using GFP–Trap confirmed that cMyc–PP1c-1 co-immunoprecipitated only with WT GFP–Pi04314. Expression of constructs in the leaves is indicated by +. Protein size markers are indicated in kDa, protein loading is indicated by Ponceau stain, and antibodies used are as indicated (αcMyc and αGFP). (c) Single optical section through co-expressing nuclei show that the mutated effector fusion GFP–Pi04314mut co-expressed with mRFP–PP1c-1 did not cause reduction of mRFP fluorescence in the nucleolus, whereas the WT GFP–Pi04314 did. Scale bar, 10 μm. White arrows indicate mRFP fluorescence intensity plots shown in graphs to the right of each image. (d) Graph shows the average ratio of nucleolar to nucleoplasmic mRFP fluorescence from the mRFP–PP1c-1 expressed alone, with the WT effector fusion GFP–Pi04314 and with the mutated effector GFP–Pi04314mut. The averages were obtained from a minimum of 30 nuclei for each sample. Error bars are s.e. and the graph represents the combined data from three biological replicates. Letters on the graph denote statistically significant differences (ANOVA, P<0.001). (e) The GFP fusion to the mutated Pi04314 is no longer able to significantly promote P. infestans infection as measured by lesion diameter. Error bars are s.e. and the graph represents the combined data from three biological replicates (n=108 per construct). Letters on the graph denote statistically significant differences (ANOVA, P≤0.022).