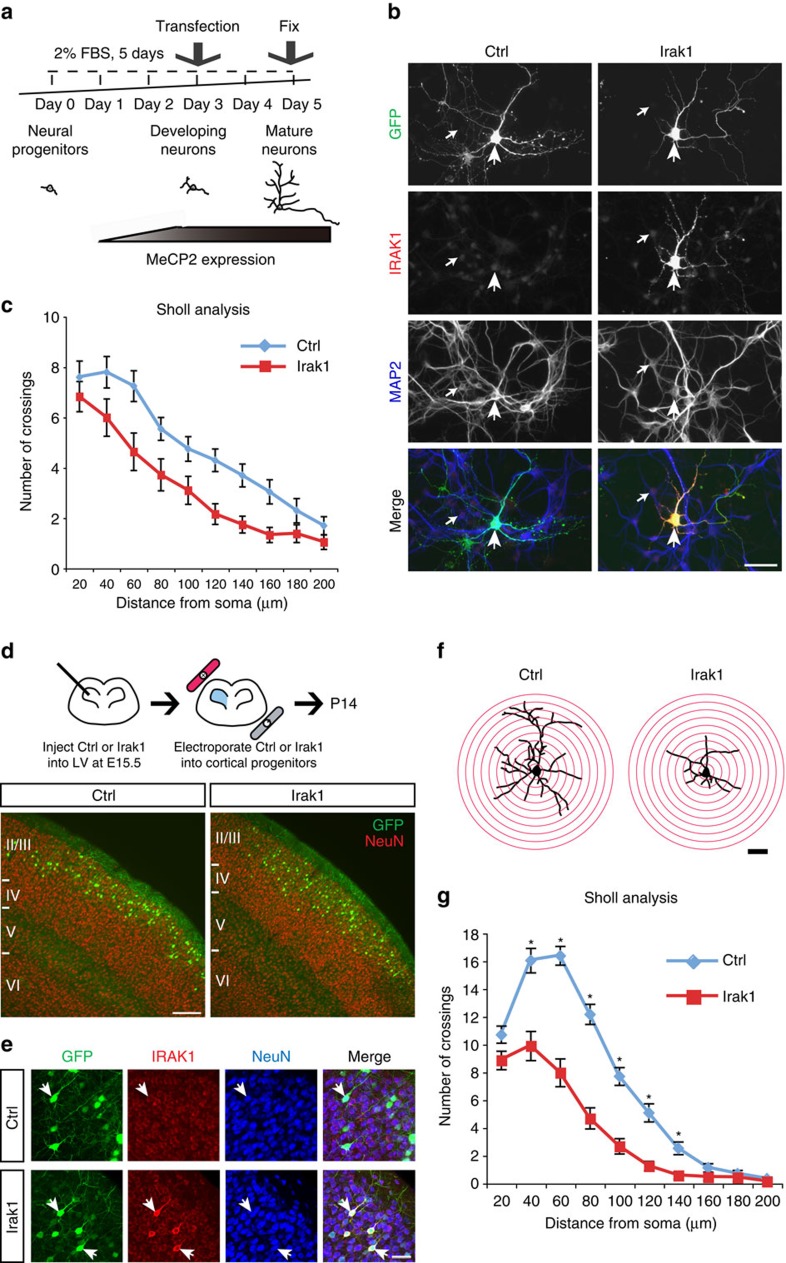
Figure 2. Overexpression of Irak1 in cortical neurons reduces dendritic arborization.
(a) A plasmid overexpressing either a reporter GFP (Ctrl) or both Irak1 and GFP (Irak1) was transfected into developing immature neurons in culture. (b) IRAK1 protein (red) is highly expressed by neurons (MAP2 positive; blue) transfected with Irak1 and GFP (green), while neurons transfected with GFP alone express only endogenous, low levels of IRAK1. Large arrowheads indicate transfected neurons; small arrows indicate neighbouring, untransfected neurons. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) Cells were immuno-labelled against both MAP2 and GFP, and the dendritic morphology of MAP2+/GFP+ cells was analysed by Sholl analysis. Overexpression of Irak1 significantly decreases neuronal dendritic arborization, compared to that of control neurons (control n=20, Irak1-overexpressing neurons n=36); two-way ANOVA, F(1,540)=39.9, P<0.001). Error bars=mean±s.e.m. (d) To investigate whether overexpression of Irak1 also modifies dendritic complexity of layer 2/3 neurons in vivo, Ctrl and Irak1 plasmids were injected in utero into the lateral ventricle (LV), and electroporated into neural precursors in the ventricular zone (VZ) at E15.5. Electroporated neural precursors subsequently give rise to differentiated cortical layer 2/3 projection neurons (NeuN+, red), with no obvious disruption in laminar location or survival at P14 with Irak1 overexpression. Scale bar, 200 μm. (e) IRAK1 protein (red) is highly overexpressed by P14 layer 2/3 neurons electroporated with Irak1, but not Ctrl, compared to endogenous IRAK1 expression within cortical layer 2/3 at P14. Scale bar, 50 μm. (f,g) We analysed the dendritic morphology of electroporated layer 2/3 projection neurons at P14 by Sholl analysis (ctrl n=24, Irak1 n=28). In vivo overexpression of Irak1 in layer 2/3 projection neurons results in reduced dendritic arborization, recapitulating the dendritic phenotype in layer 2/3 projection neurons in Mecp2-null mice. *P<0.01, a two-way ANOVA and the Bonferroni test, mean±s.e.m., Scale bars, 50 μm.